Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Acute Crit Care > Volume 38(2); 2023 > Article
-
Original Article
Meta-analysis Comparison of safety and efficacy between therapeutic or intermediate versus prophylactic anticoagulation for thrombosis in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis -
Hyeon-Jeong Lee1
 , Hye Jin Jang2
, Hye Jin Jang2 , Won-Il Choi2
, Won-Il Choi2 , Joonsung Joh3
, Joonsung Joh3 , Junghyun Kim3
, Junghyun Kim3 , Jungeun Park1
, Jungeun Park1 , Miyoung Choi1
, Miyoung Choi1
-
Acute and Critical Care 2023;38(2):160-171.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4266/acc.2022.01424
Published online: May 25, 2023
1Division of Healthcare Technology Assessment Research, National Evidence-based Healthcare Collaborating Agency, Seoul, Korea
2Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Myongji Hospital, Hanyang University, Korea
3Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, National Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- Corresponding author: Miyoung Choi Division of Healthcare Technology Assessment Research, National Evidence-based Healthcare Collaborating Agency, Health and Welfare Administration Town, 400 Neungdong-ro, Gwangjin-gu, Seoul 04933, Korea Tel: +82-2-2174-2867, Fax: +82-2-747-4916, Email: myhams95@gmail.com
- *These authors contributed equally to this work.
Copyright © 2023 The Korean Society of Critical Care Medicine
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
-
Background
- Patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infections often have macrovascular or microvascular thrombosis and inflammation, which are known to be associated with a poor prognosis. Heparin has been hypothesized that administration of heparin with treatment dose rather than prophylactic dose for prevention of deep vein thrombosis in COVID-19 patients.
-
Methods
- Studies comparing therapeutic or intermediate anticoagulation with prophylactic anticoagulation in COVID-19 patients were eligible. Mortality, thromboembolic events, and bleeding were the primary outcomes. PubMed, Embase, the Cochrane Library, and KMbase were searched up to July 2021. A meta-analysis was performed using random-effect model. Subgroup analysis was conducted according to disease severity.
-
Results
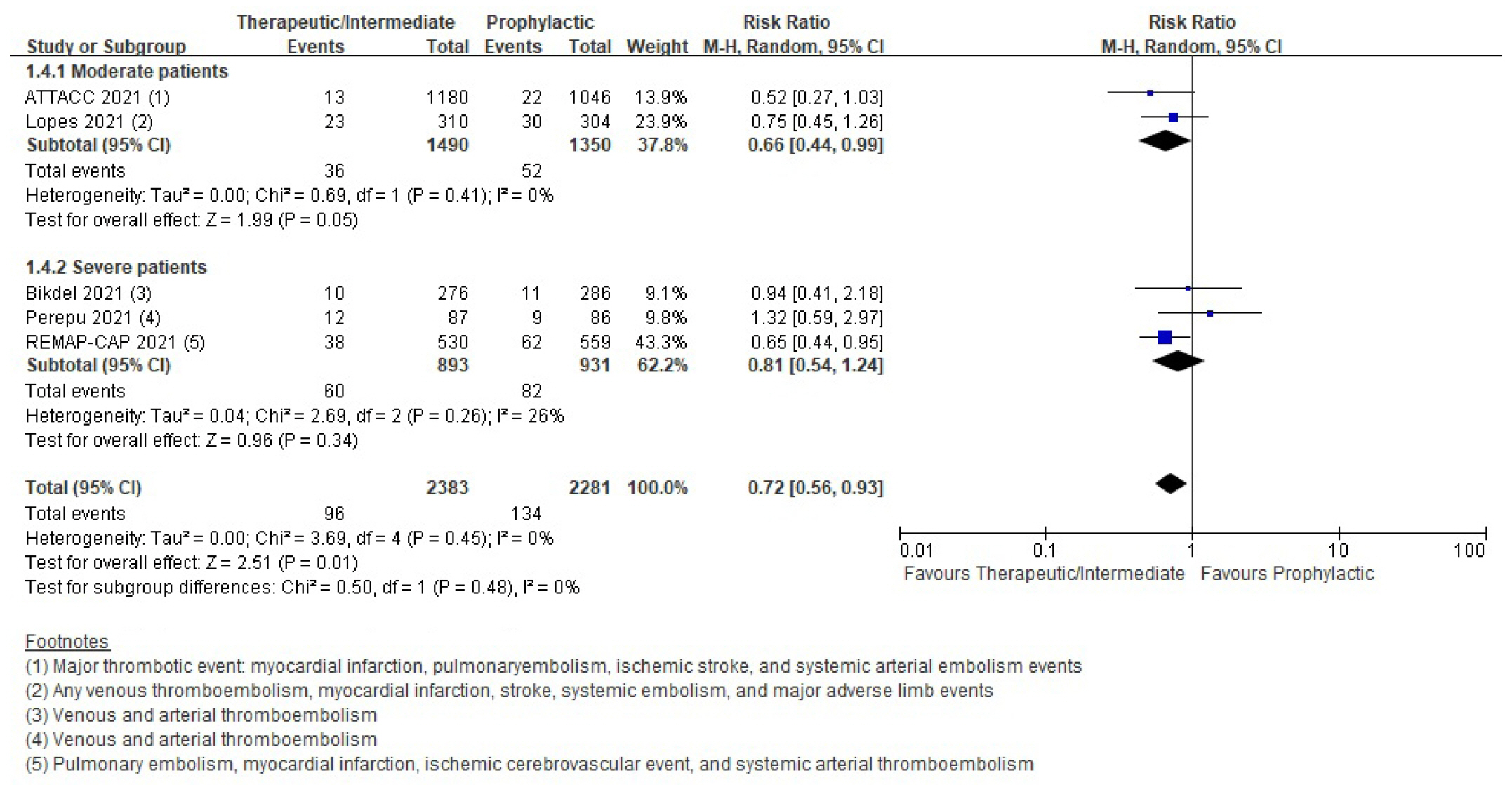
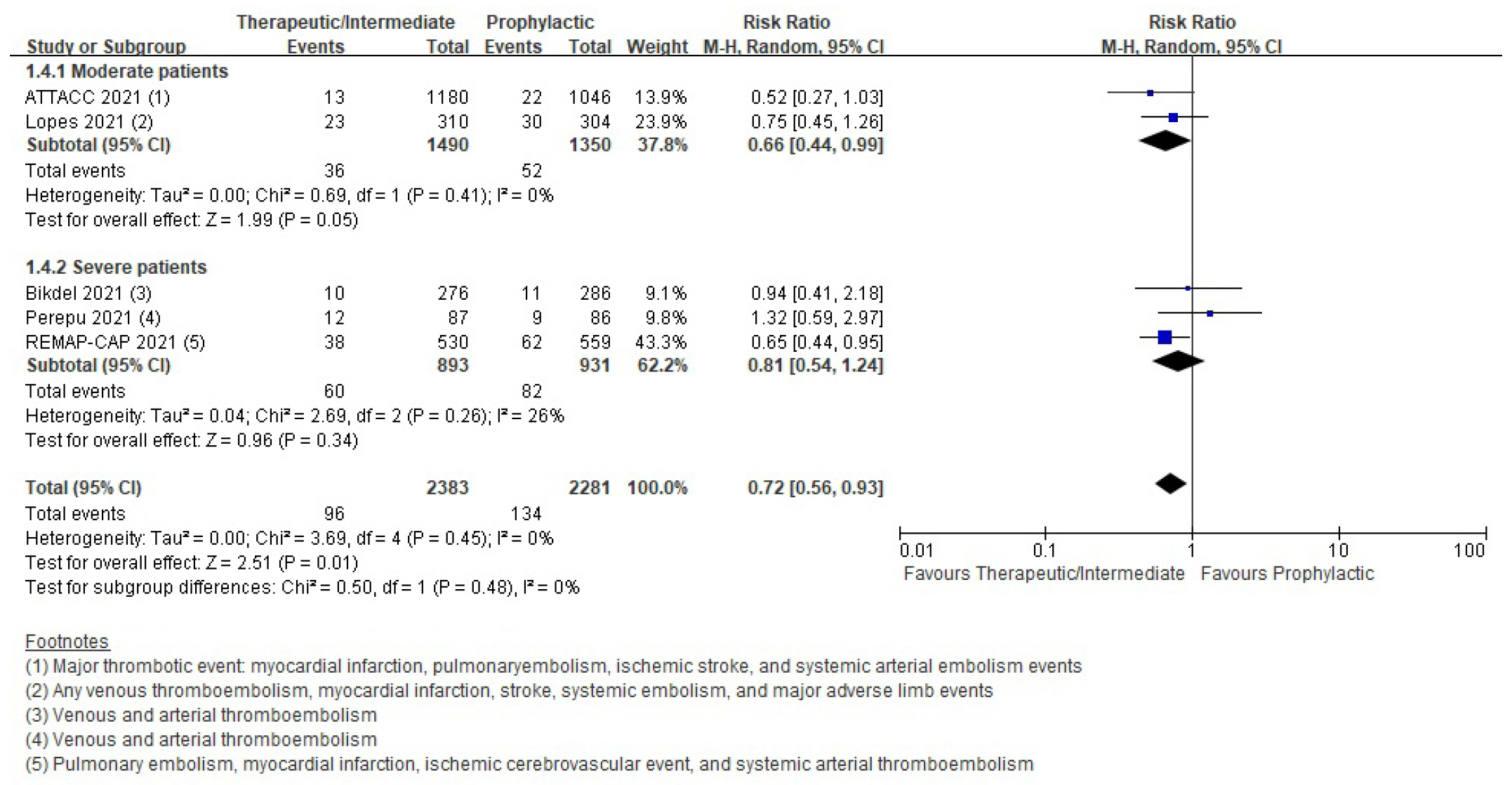
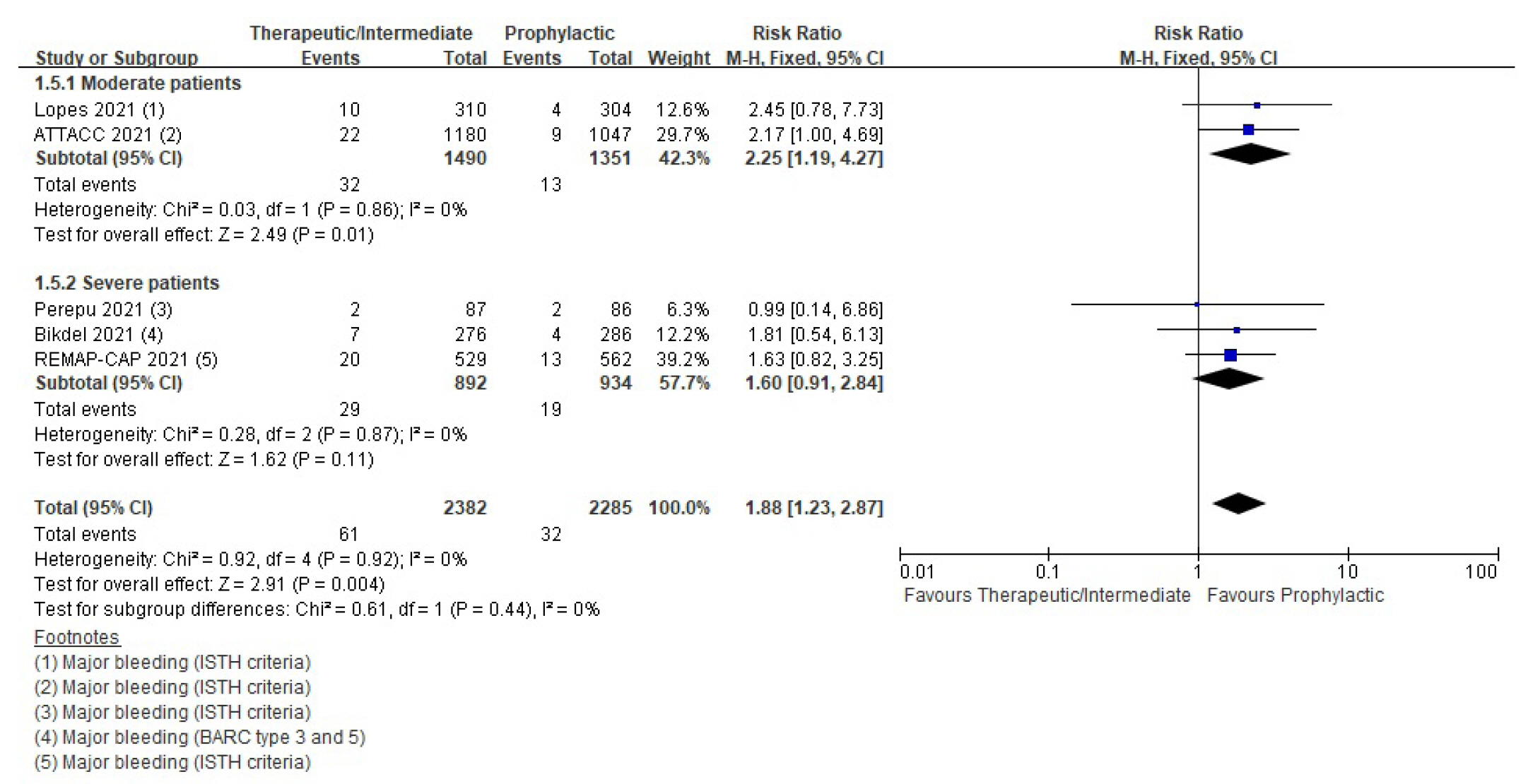
- Six randomized controlled trials (RCTs) with 4,678 patients and four cohort studies with 1,080 patients were included in this review. In the RCTs, the therapeutic or intermediate anticoagulation was associated with significant reductions in the occurrence of thromboembolic events (5 studies, n=4,664; relative risk [RR], 0.72; P=0.01), and a significant increase in bleeding events (5 studies, n=4,667; RR, 1.88; P=0.004). In the moderate patients, therapeutic or intermediate anticoagulation was more beneficial than prophylactic anticoagulation in terms of thromboembolic events, but showed significantly higher bleeding events. In the severe patients, the incidence of thromboembolic and bleeding events in the therapeutic or intermediate.
-
Conclusions
- The study findings suggest that prophylactic anticoagulant treatment should be used in patients with moderate and severe COVID-19 infection groups. Further studies are needed to determine more individualized anticoagulation guidance for all COVID-19 patients.
INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
RESULTS
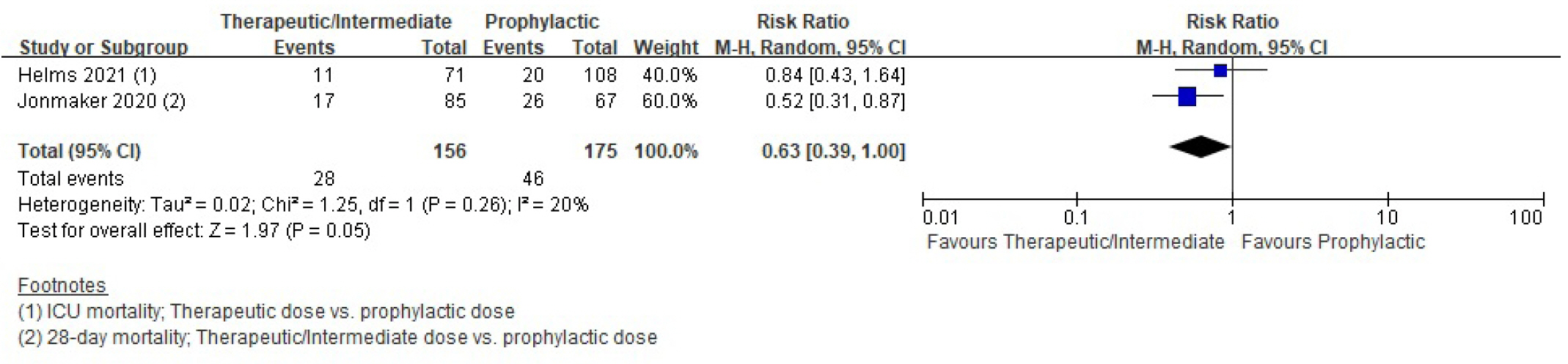
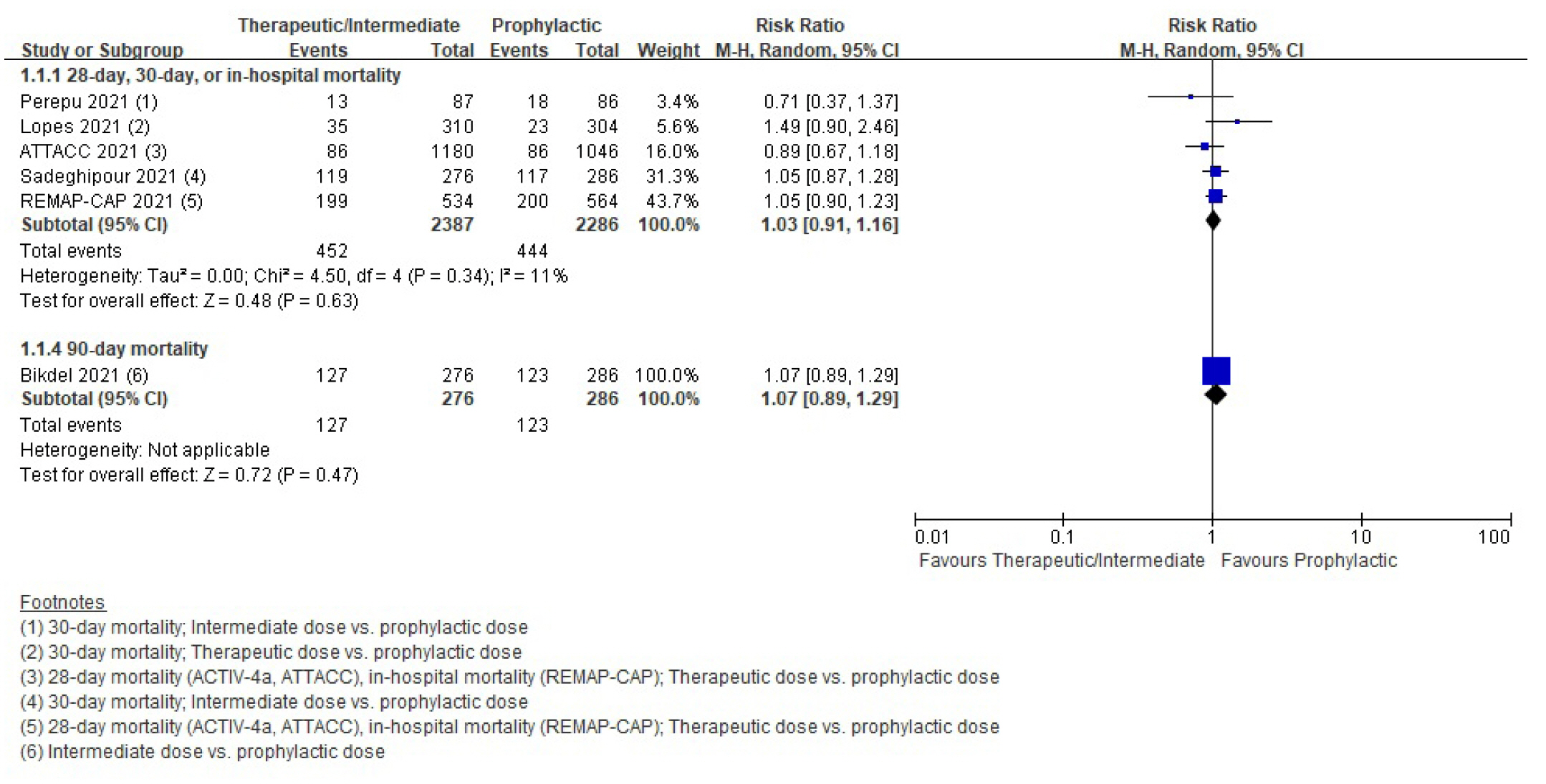
Mortality
Thromboembolic events
Bleeding
DISCUSSION
KEY MESSAGES
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
-
FUNDING
This study was supported by the National Evidence-based Healthcare Collaborating Agency (project no. NP21-004 and NA22-009/NA23-009).
-
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conceptualization: HJL, HJJ, MC. Methodology: MC. Formal analysis: HJL, HJJ, JK. Data curation: HJL, HJJ, WC, JJ. Visualization: JP. Project administration: MC, JP. Funding acquisition: MC. Writing–original draft: HJL, HJJ. Writing–review & editing: MC, WC, JJ, JK, JP.
NOTES
Acknowledgments
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
Supplementary Table 3.
Supplementary Figure 1.
Supplementary Figure 2.
Supplementary Figure 3.
Supplementary Figure 4.
Supplementary Figure 5.
Supplementary Figure 6.
Supplementary Figure 7.
Supplementary Figure 8.



| First author (study) | Year | Study design | Country | Setting | Severity | Sample size (intervention/control) |
Anticoagulation |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intervention | Control | |||||||
| ATTACC investigators [15] | 2021 | RCT (REMAP-CAP, ACTIV-4a, ATTACC) | US, Canada, UK, Brazil, Mexico, Nepal, Australia, Netherlands, Spain | Multicenter | Moderate | 1,181/1,050 | Therapeutic dose | Prophylactic dose |
| - LMWH, according to patient weight | - According to local guidelines or usual practice | |||||||
| REMAP-CAP Investigators [19] | 2021 | - | Severe | 534/564 | - Alternative UFH, target for aPTT 1.5–2.5 times the upper limit of normal or anti-Xa levels (0.3–0.7 IU/ml) | - | ||
| Bikdeli [16], Sadeghipour [20] | 2021 | RCT (INSPIRATION) | Iran | Multicenter | Severe | 276/286 | Intermediate dose | Prophylactic dose |
| - Enoxaparin 1 mg/kg qd sc | - Enoxaparin 40 mg qd sc | |||||||
| - UFH 10,000 units bid, if severe kidney insufficiency | - UFH 5,000 units bid, if severe kidney insufficiency | |||||||
| Lopes [17] | 2021 | RCT (ACTION) | Brazil | Multicenter | Moderate | 310/304 | Therapeutic dose | Prophylactic dose |
| - Rivaroxaban 15–20 mg qd po | - Standard venous prophylaxis with enoxaparin or unfractionated heparin | |||||||
| - Enoxaparin 1 mg/kg bid or UFH, target for aPTT 1.5–2.5 times the mean normal level or anti-Xa levels (0.3–0.7 IU/ml) if clinically unstable patients | ||||||||
| Perepu [18] | 2021 | RCT | US | Multicenter | Severe | 87/86 | Intermediate dose | Prophylactic dose |
| - Enoxaparin 1 mg/kg qd sc | - Enoxaparin 30–40 mg bid sc | |||||||
| Helms [21] | 2021 | Retrospective cohort study | France | Multicenter | Severe | 71/108 | Therapeutic dose | Prophylactic dose |
| - LMWH 100 IU/kg bid sc, not exceeding 10,000 IU/12 hr | - Enoxaparin ≤6,000 IU bid | |||||||
| - UFH 500 IU/kg qd, if creatinine clearance <30 ml/min | - UFH 200 IU/kg qd, if creatinine clearance <30 ml/min | |||||||
| Taccone [24] | 2020 | Retrospective cohort study | Belgium | Single center | Severe | 18/22 | Therapeutic dose | Prophylactic dose |
| - Enoxaparin 4,000 IU bid sc | - Enoxaparin 4,000 IU qd sc | |||||||
| - UFH 1,500–2,200 IU/hr continuous infusion, in case of RRT and/or ECMO | ||||||||
| Lavinio [23] | 2021 | Retrospective cohort study | UK, Italy, Spain, Belgium, Austria | Multicenter | Severe | 274/435 | Therapeutic dose | Prophylactic dose |
| - Enoxaparin 50–100 IU/kg bid | - Not reported | |||||||
| Jonmarker [22] | 2020 | Retrospective cohort study | Sweden | Single center | Severe | 85/67 | Therapeutic dose (n=37) | Prophylactic dose |
| - Tinzaparin ≥175 IU/kg or Dalteparin ≥200 IU/kg | -Tinzaparin 2,500–4,500 IU or Dalteparin 2,500–5,000 IU | |||||||
| Intermediate dose (n=48) | ||||||||
| - Tinzaparin >4,500 IU but <175 IU/kg or Dalteparin >5,000 IU but <200 IU/kg | ||||||||
| Outcome | Study design |
Anticipated absolute effect (95% CI) |
Relative risk (95% CI) | No. of participants (studies) | Certainty of the evidence | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risk with thromboprophylaxis | Risk with therapeutic anticoagulation | (GRADE) | ||||
| 28-Day, 30-day, ICU, or in-hospital mortality | RCT | 194 Per 1,000 | 200 Per 1,000 (177–225) | 1.03 (0.91–1.16) | 4,673 (5) | ⨁⨁⨁◯ |
| Moderatea) | ||||||
| Cohort study | 263 Per 1,000 | 166 Per 1,000 (13–263) | 0.63 (0.39–1.00) | 331 (2) | ⨁◯◯◯ | |
| Lavinio et al. [23] reported therapeutic dose of anticoagulants was associated with significant reduction in ICU mortality compared to prophylactic dose (log odds, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.18–1.1; P=0.0069). | 709 (1) | Very lowb),c) | ||||
| Thromboembolic event | RCT | 59 Per 1,000 | 42 Per 1,000 (33–55) | 0.72 (0.56–0.93) | 4,664 (5) | ⨁⨁⨁◯ |
| Moderatea) | ||||||
| Cohort study | 207 Per 1,000 | 139 Per 1,000 (70–273) | 0.67 (0.34–1.32) | 1,043 (4) | ⨁◯◯◯ | |
| Very lowb),d) | ||||||
| Bleeding | RCT | 14 Per 1,000 | 26 Per 1,000 (17–40) | 1.88 (1.23–2.87) | 4,667 (5) | ⨁⨁⨁◯ |
| Moderatea) | ||||||
| Cohort study | 52 Per 1,000 | 40 Per 1,000 (22–72) | 0.69 (0.38–1.25) | 1,040 (3) | ⨁◯◯◯ | |
| Very lowb),c) | ||||||
CI: confidence interval; GRADE: Grading of Recommendations Assessment Development and Evaluation; ICU: intensive care unit; RCT: randomized clinical trial.
a) One study has heterogeneity regarding anticoagulants dose;
b) Overall serious risk of bias across studies
c) Imprecision due to limited sample size;
d) Very few events in both intervention and control group.
- 1. Godoy LC, Goligher EC, Lawler PR, Slutsky AS, Zarychanski R. Anticipating and managing coagulopathy and thrombotic manifestations of severe COVID-19. CMAJ 2020;192:E1156-61.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 2. Bilaloglu S, Aphinyanaphongs Y, Jones S, Iturrate E, Hochman J, Berger JS. Thrombosis in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in a New York City health system. JAMA 2020;324:799-801.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 3. McGonagle D, O’Donnell JS, Sharif K, Emery P, Bridgewood C. Immune mechanisms of pulmonary intravascular coagulopathy in COVID-19 pneumonia. Lancet Rheumatol 2020;2:e437-45.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 4. Llitjos JF, Leclerc M, Chochois C, Monsallier JM, Ramakers M, Auvray M, et al. High incidence of venous thromboembolic events in anticoagulated severe COVID-19 patients. J Thromb Haemost 2020;18:1743-6.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 5. Miesbach W, Makris M. COVID-19: coagulopathy, risk of thrombosis, and the rationale for anticoagulation. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 2020;26:1076029620938149. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 6. Connors JM, Levy JH. COVID-19 and its implications for thrombosis and anticoagulation. Blood 2020;135:2033-40.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 7. Clausen TM, Sandoval DR, Spliid CB, Pihl J, Perrett HR, Painter CD, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection depends on cellular heparan sulfate and ACE2. Cell 2020;183:1043-57.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 8. Buijsers B, Yanginlar C, Maciej-Hulme ML, de Mast Q, van der Vlag J. Beneficial non-anticoagulant mechanisms underlying heparin treatment of COVID-19 patients. EBioMedicine 2020;59:102969. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 9. Mycroft-West CJ, Su D, Pagani I, Rudd TR, Elli S, Gandhi NS, et al. Heparin inhibits cellular invasion by SARS-CoV-2: structural dependence of the interaction of the spike S1 receptor-binding domain with heparin. Thromb Haemost 2020;120:1700-15.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 10. Page MJ, Moher D, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021;372:n160. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 11. Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Chandler J, Welch VA, Higgins JP, et al. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: a new edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2019;10:ED000142.ArticlePubMed
- 12. Kim SY, Seo HJ, Lee YJ, Park JE. Study design algorithm for medical literature of intervention (DAMI) and Risk of Bias for Nonrandomized Studies (RoBANS) ver 2.0 by HIRA. Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service. 2013.
- 13. Kim SY, Park JE, Lee YJ, Seo HJ, Sheen SS, Hahn S, et al. Testing a tool for assessing the risk of bias for nonrandomized studies showed moderate reliability and promising validity. J Clin Epidemiol 2013;66:408-14.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Balshem H, Helfand M, Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines: 3. Rating the quality of evidence. J Clin Epidemiol 2011;64:401-6.ArticlePubMed
- 15. ATTACC Investigators; ACTIV-4a Investigators; REMAP-CAP Investigators; Lawler PR, Goligher EC, Berger JS, et al. Therapeutic anticoagulation with heparin in noncritically ill patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med 2021;385:790-802.ArticlePubMed
- 16. Bikdeli B, Talasaz AH, Rashidi F, Bakhshandeh H, Rafiee F, Rezaeifar P, et al. Intermediate-dose versus standard-dose prophylactic anticoagulation in patients with COVID-19 admitted to the intensive care unit: 90-day results from the INSPIRATION randomized trial. Thromb Haemost 2022;122:131-41.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Lopes RD, de Barros E Silva PG, Furtado RH, Macedo AV, Bronhara B, Damiani LP, et al. Therapeutic versus prophylactic anticoagulation for patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 and elevated D-dimer concentration (ACTION): an open-label, multicentre, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet 2021;397:2253-63.PubMedPMC
- 18. Perepu US, Chambers I, Wahab A, Ten Eyck P, Wu C, Dayal S, et al. Standard prophylactic versus intermediate dose enoxaparin in adults with severe COVID-19: a multi-center, open-label, randomized controlled trial. J Thromb Haemost 2021;19:2225-34.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 19. REMAP-CAP Investigators; ACTIV-4a Investigators; ATTACC Investigators; Goligher EC, Bradbury CA, McVerry BJ, et al. Therapeutic anticoagulation with heparin in critically ill patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med 2021;385:777-89.ArticlePubMed
- 20. INSPIRATION Investigators; Sadeghipour P, Talasaz AH, Rashidi F, Sharif-Kashani B, Beigmohammadi MT, et al. Effect of intermediate-dose vs standard-dose prophylactic anticoagulation on thrombotic events, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation treatment, or mortality among patients with COVID-19 admitted to the intensive care unit: the INSPIRATION randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2021;325:1620-30.PubMed
- 21. Helms J, Severac F, Merdji H, Schenck M, Clere-Jehl R, Baldacini M, et al. Higher anticoagulation targets and risk of thrombotic events in severe COVID-19 patients: bi-center cohort study. Ann Intensive Care 2021;11:14. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 22. Jonmarker S, Hollenberg J, Dahlberg M, Stackelberg O, Litorell J, Everhov ÅH, et al. Dosing of thromboprophylaxis and mortality in critically ill COVID-19 patients. Crit Care 2020;24:653. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 23. Lavinio A, Ercole A, Battaglini D, Magnoni S, Badenes R, Taccone FS, et al. Safety profile of enhanced thromboprophylaxis strategies for critically ill COVID-19 patients during the first wave of the pandemic: observational report from 28 European intensive care units. Crit Care 2021;25:155. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 24. Taccone FS, Gevenois PA, Peluso L, Pletchette Z, Lheureux O, Brasseur A, et al. Higher intensity thromboprophylaxis regimens and pulmonary embolism in critically ill coronavirus disease 2019 patients. Crit Care Med 2020;48:e1087-90.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Vincent JL, Levi M, Hunt BJ. Prevention and management of thrombosis in hospitalised patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. Lancet Respir Med 2022;10:214-20.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Poor HD. Pulmonary thrombosis and thromboembolism in COVID-19. Chest 2021;160:1471-80.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Ma Z, Yang KY, Huang Y, Lui KO. Endothelial contribution to COVID-19: an update on mechanisms and therapeutic implications. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2022;164:69-82.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Phung OJ, Kahn SR, Cook DJ, Murad MH. Dosing frequency of unfractionated heparin thromboprophylaxis: a meta-analysis. Chest 2011;140:374-81.ArticlePubMed
- 29. Kleber FX, Witt C, Vogel G, Koppenhagen K, Schomaker U, Flosbach CW, et al. Randomized comparison of enoxaparin with unfractionated heparin for the prevention of venous thromboembolism in medical patients with heart failure or severe respiratory disease. Am Heart J 2003;145:614-21.ArticlePubMed
- 30. Bergmann JF, Neuhart E. A multicenter randomized double-blind study of enoxaparin compared with unfractionated heparin in the prevention of venous thromboembolic disease in elderly in-patients bedridden for an acute medical illness. Thromb Haemost 1996;76:529-34.ArticlePubMed
- 31. Forette B, Wolmark Y. Calcium nadroparin in the prevention of thromboembolic disease in elderly subjects: study of tolerance. Presse Med 1995;24:567-71.PubMed
- 32. Cohen AT, Spiro TE, Büller HR, Haskell L, Hu D, Hull R, et al. Rivaroxaban for thromboprophylaxis in acutely ill medical patients. N Engl J Med 2013;368:513-23.ArticlePubMed
- 33. Cohen AT, Harrington RA, Goldhaber SZ, Hull RD, Wiens BL, Gold A, et al. Extended thromboprophylaxis with betrixaban in acutely ill medical patients. N Engl J Med 2016;375:534-44.ArticlePubMed
- 34. Decousus H, Tapson VF, Bergmann JF, Chong BH, Froehlich JB, Kakkar AK, et al. Factors at admission associated with bleeding risk in medical patients: findings from the IMPROVE investigators. Chest 2011;139:69-79.ArticlePubMed
- 35. Schulman S, Sholzberg M, Spyropoulos AC, Zarychanski R, Resnick HE, Bradbury CA, et al. ISTH guidelines for antithrombotic treatment in COVID-19. J Thromb Haemost 2022;20:2214-25.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 36. Spyropoulos AC, Levy JH, Ageno W, Connors JM, Hunt BJ, Iba T, et al. Scientific and Standardization Committee communication: clinical guidance on the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of venous thromboembolism in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. J Thromb Haemost 2020;18:1859-65.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 37. Cuker A, Tseng EK, Nieuwlaat R, Angchaisuksiri P, Blair C, Dane K, et al. American Society of Hematology living guidelines on the use of anticoagulation for thromboprophylaxis in patients with COVID-19: January 2022 update on the use of therapeutic-intensity anticoagulation in acutely ill patients. Blood Adv 2022;6:4915-23.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 38. Panel CT. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) treatment guidelines [Internet]. National Institutes of Health. 2023;[cited 2023 Feb 1]. Available from: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/.
- 39. National Evidence-based Healthcare Collaborating Agency (NECA). Korean COVID-19 living guideline: anticoagulant recommendations [Internet]. NECA. 2022;[cited 2023 Feb 1]. Available from: https://www.neca.re.kr/lay1/bbs/S1T11C174/F/58/view.do?article_seq=9067&cpage=1&rows=10000&condition=&keyword=&show=&cat.
References
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- The Community Pharmacy as a Study Center for the Epidemiological Analysis of the Population Vaccination against SARS-CoV-2: Evaluation of Vaccine Safety and Pharmaceutical Service
Jacopo Raffaele Dibenedetto, Michela Cetrone, Marina Antonacci, Domenico Pio Cannone, Stefania Antonacci, Pasquale Bratta, Francesco Leonetti, Domenico Tricarico
Pharmacy.2024; 12(1): 16. CrossRef - Specific and Non-specific Aspects and Future Challenges of ICU Care Among COVID-19 Patients with Obesity: A Narrative Review
Alexandra Beurton, Emma J. Kooistra, Audrey De Jong, Helmut Schiffl, Mercedes Jourdain, Bruno Garcia, Damien Vimpère, Samir Jaber, Peter Pickkers, Laurent Papazian
Current Obesity Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Figure
- We recommend
- Related articles
-
- Comparison of safety and efficacy between therapeutic or intermediate versus prophylactic anticoagulation for thrombosis in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Comparison of high-flow nasal oxygen therapy and noninvasive ventilation in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis

 KSCCM
KSCCM
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite