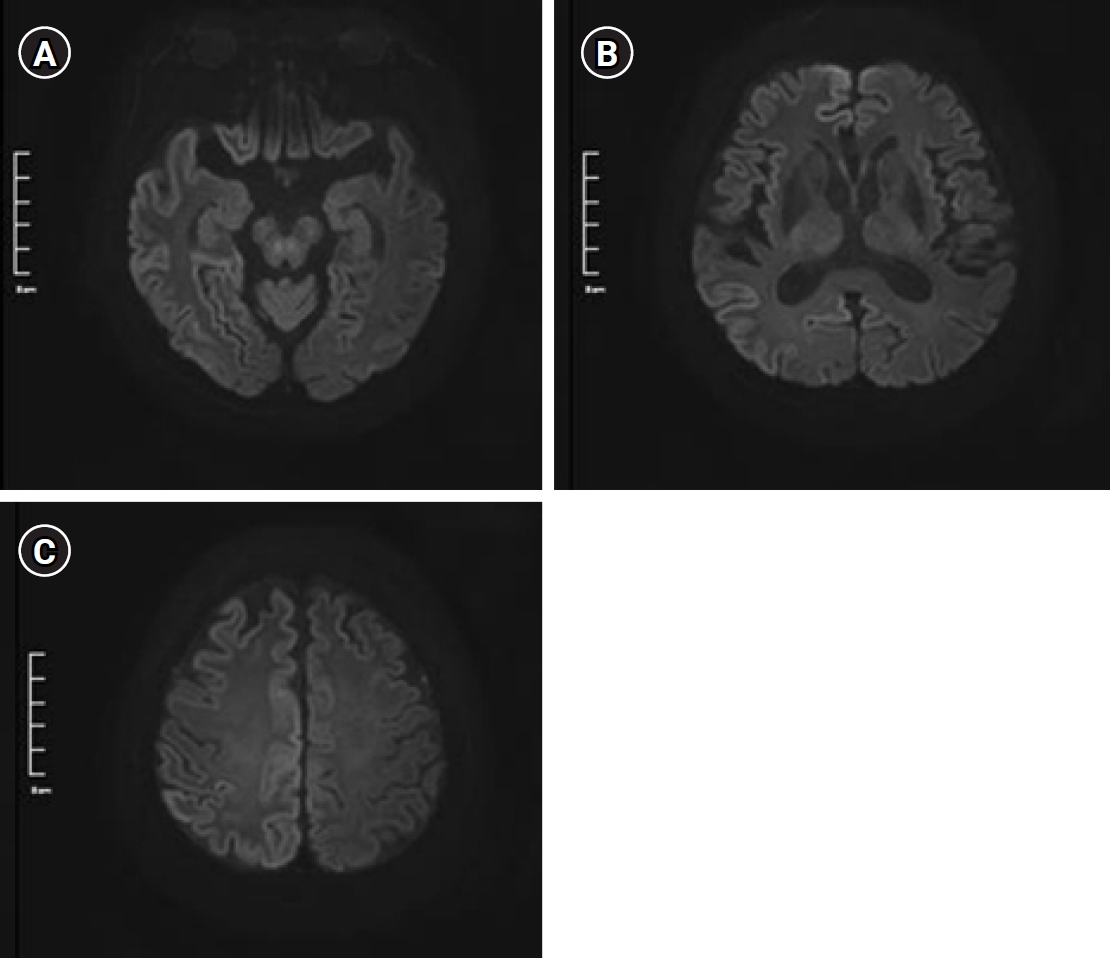
Contrast media mimicking subarachnoid hemorrhage after intrathecal injection in a patient with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
Article information
Acute Crit Care. 2022;37(4):693-693
Publication date (electronic) : 2022 November 30
doi :
https://doi.org/10.4266/acc.2022.00339.e1
Received 2022 September 30; Revised 2022 September 30; Accepted 2022 September 30.
Acute and Critical Care 2022;37:474-476
https://doi.org/10.4266/acc.2022.00339
In the article entitled “Contrast media mimicking subarachnoid hemorrhage after intrathecal injection in a patient with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease”, the figure legend was incorrectly presented. The correct figure is as follows.
Article information Continued
Copyright © 2022 The Korean Society of Critical Care Medicine