Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Acute Crit Care > Volume 34(1); 2019 > Article
-
Original Article
Pulmonary Protecting Postextubation Respiratory Failure and Reintubation by High-Flow Nasal Cannula Compared to Low-Flow Oxygen System: Single Center Retrospective Study and Literature Review -
Minhyeok Lee1,2
 , Ji Hye Kim1
, Ji Hye Kim1 , In Beom Jeong1
, In Beom Jeong1 , Ji Woong Son1
, Ji Woong Son1 , Moon Jun Na1
, Moon Jun Na1 , Sun Jung Kwon1
, Sun Jung Kwon1
-
Acute and Critical Care 2019;34(1):60-70.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4266/acc.2018.00311
Published online: February 28, 2019
1Division of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Konyang University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea
2The 2nd Infantry Division of Republic of Korea Army, Yanggu, Korea
- Corresponding author Sun Jung Kwon Division of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Konyang University Hospital, 158 Gwanjeodong-ro, Seo-gu, Daejeon 35365, Korea Tel: +82-42-600-8820 Fax: +82-42-600-9100 E-mail: sjoongkwon@hanmail.net
Copyright © 2019 The Korean Society of Critical Care Medicine
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Abstract
-
Background
- Use of a high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) reduced postextubation respiratory failure (PERF) and reintubation rate compared to use of a low-flow oxygen system (LFOS) in low-risk patients. However, no obvious conclusion was reached for high-risk patients. Here, we sought to present the current status of HFNC use as adjunctive oxygen therapy in a clinical setting and to elucidate the nature of the protective effect following extubation.
-
Methods
- The medical records of 855 patients who were admitted to the intensive care unit of single university hospital during a period of 5.5 years were analyzed retrospectively, with only 118 patients ultimately included in the present research. The baseline characteristics of these patients and the occurrence of PERF and reintubation along with physiologic changes were analyzed.
-
Results
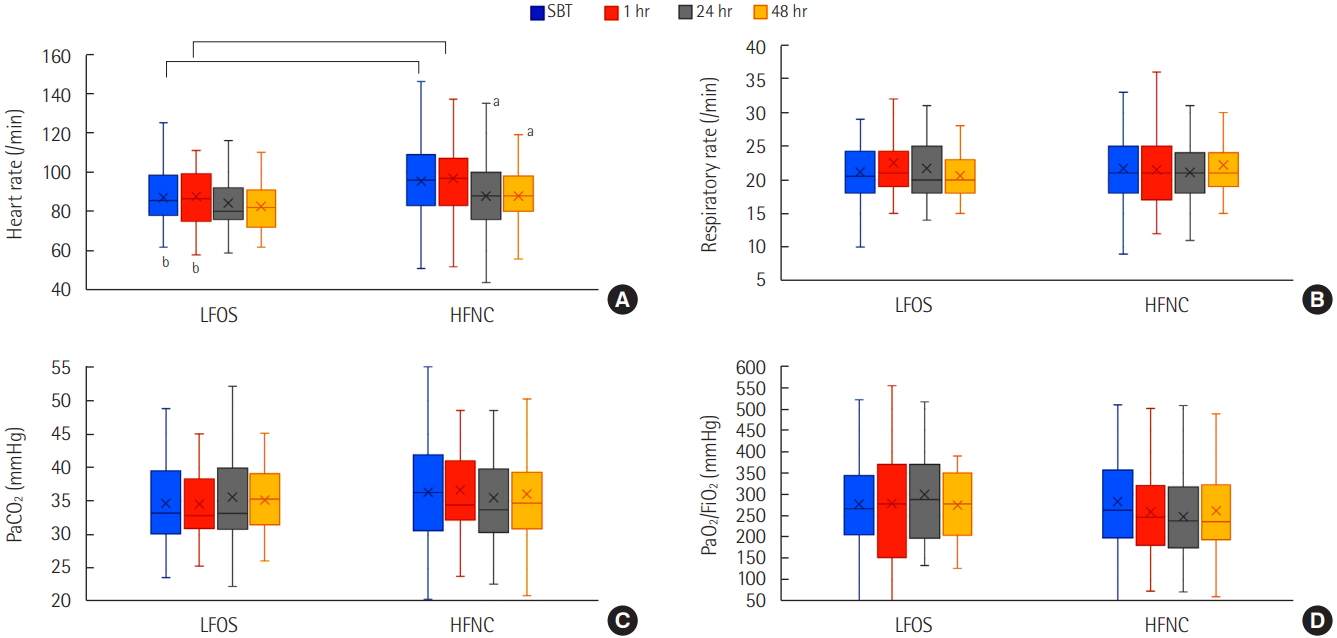
- Eighty-four patients underwent HFNC, and the remaining 34 patients underwent conventional LFOS after extubation. Physicians preferred HFNC to LFOS in the face of high-risk features including old age, neurologic disease, moderate to severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, a long duration of mechanical ventilation, low baseline arterial partial pressure of oxygen to fraction of inspired oxygen ratio, and a high baseline alveolar–arterial oxygen difference. The reintubation rate at 72 hours after extubation was not different (9.5% vs. 8.8%; P=1.000). Hypoxic respiratory failure was slightly higher in the nonreintubation group than in the reintubation group (31.9% vs. 6.7%; P=0.058). Regarding physiologic effects, heart rate was only stabilized after 24 hours of extubation in the HFNC group.
-
Conclusions
- No difference was found in the occurrence of PERF and reintubation between both groups. It is worth noting that similar PERF and reintubation ratios were shown in the HFNC group in those with certain exacerbating risk factors versus not. Caution is needed regarding delayed reintubation in the HFNC group.
INTRODUCTION
MATERIALS AND METHODS
RESULTS
DISCUSSION
HIGHLIGHTS
-
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
-
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conceptualization: SJK. Data curation: ML. Formal analysis: ML. Methodology: SJK. Visualization: ML. Writing - original draft: ML. Writing - review & editing: JHK, IBJ, JWS, MJN, SJK.
NOTES
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS

| Characteristics | HFNC (n=84) | LFOS (n=34) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male sex | 60 (71.4) | 20 (58.8) | 0.184 |
| Age (yr) | 73.0 (66.0–80.0) | 71.00 (55.75–81.25) | 0.454 |
| Height (cm) | 163.5 (158.0–170.0) | 155.50 (160.00–169.50) | 0.248 |
| Body weight (kg) | 56.65 (50.0–68.0) | 58.00 (52.00–65.00) | 0.983 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 22.0 (18.8–24.5) | 23.11 (19.44–24.92) | 0.703 |
| Underlying disease | |||
| Diabetes mellitus | 19 (22.6) | 6 (17.6) | 0.549 |
| Hypertension | 31 (36.9) | 12 (35.3) | 0.869 |
| Malignant disease | 10 (11.9) | 4 (11.8) | 1.000a |
| Chronic respiratory disease | 47 (56.0) | 15 (44.1) | 0.244 |
| Chronic heart disease | 22 (26.2) | 7 (20.6) | 0.522a |
| Chronic liver disease | 1 (1.2) | 0 | 1.000a |
| Chronic renal disease | 11 (13.1) | 3 (8.8) | 0.755a |
| Neurologic disease | 27 (32.1) | 4 (11.8) | 0.023 |
| Cause of mechanical ventilation | |||
| Pneumonia | 45 (53.6) | 19 (55.9) | 0.819 |
| Airway disease | 13 (15.5) | 3 (8.8) | 0.119 |
| Hemoptysis | 3 (3.6) | 1 (2.9) | 1.000a |
| Drug intoxication | 14 (16.7) | 10 (29.4) | 0.119 |
| Post operation | 2 (2.4) | 0 | 1.000a |
| Heat failure | 3 (3.6) | 0 | 0.556a |
| Others | 4 (4.8) | 1 (2.9) | 1.000a |
| Type of respiratory failure at intubationb | |||
| Tachypneic respiratory failure | 6 (7.1) | 2 (5.9) | 1.000a |
| Hypercapnic respiratory failure | 38 (45.2) | 12 (35.3) | 0.322 |
| Hypoxic respiratory failure | 23 (27.4) | 6 (17.6) | 0.266a |
| Othersc | 22 (26.2) | 14 (41.2) | 0.109 |
| Severity index | |||
| APACHE II score at ICU admission | 22.0 (18.00–25.00) | 22.00 (19.00–25.25) | 0.466 |
| APACHE II score at extubation | 17.0 (14.0–19.0) | 16.50 (14.00–19.00) | 0.466 |
| Vital sign and arterial blood gas before intubation | |||
| Heart rate | 100.00 (85.00–120.00) | 107.50 (85.75–121.00) | 0.861 |
| Respiratory rate | 22.00 (18.00–27.50) | 22.00 (18.75–27.25) | 0.696 |
| PaCO2 (mmHg) | 41.75 (31.72–60.97) | 39.15 (32.15–53.55) | 0.671 |
| PaO2/FiO2 (mmHg) | 130.78 (83.76–259.29) | 255.71 (200.05–320.44) | 0.001 |
| (A–a) DO2 | 183.25 (50.71–412.68) | 56.12 (21.37–166.99) | 0.003 |
| Vital sign and arterial blood gas before extubation | |||
| Heart rate on ventilation | 84.50 (74.25–101.75) | 85.00 (68.00–90.25) | 0.198 |
| Respiratory rate on ventilation | 18.00 (16.00–21.00) | 17.00 (15.00–20.00) | 0.155 |
| PaCO2 on ventilation (mmHg) | 34.75 (30.05–40.35) | 34.40 (28.70–36.15) | 0.051 |
| PaO2/FiO2 on ventilation (mmHg) | 288.00 (208.31–363.81) | 333.75 (279.37–379.37) | 0.069 |
| (A-a) DO2 at spontaneous breathing trial | 138.71 (95.60–167.74) | 130.20 (88.29–130.20) | 0.478 |
| High risk patient | |||
| Age older than 65 years | 65 (77.4) | 20 (58.8) | 0.042 |
| Body mass index higher than 30 kg/m2 | 7 (8.3) | 2 (5.9) | 1.000a |
| Ventilator duration more than 7 days | 30 (35.7) | 7 (20.6) | 0.109 |
| Charlson comorbidity index of 2 or more | 33 (39.3) | 7 (20.6) | 0.052 |
| APACHE II score of more than 12 | 80 (95.2) | 32 (94.1) | 0.802 |
| Heart failure as a cause of intubation | 3 (3.6) | 0 | 0.556a |
| Moderate to severe COPD | 16 (19.0) | 0 | 0.005a |
| Failure with first SBT trial | 52 (61.9) | 17 (50.0) | 0.235 |
| Duration of mechanical ventilation before extubation (hr) | 120.3 (74.9–213.8) | 81.93 (47.45–139.09) | 0.012 |
| Hospital day before extubation trial (day) | 7.5 (4.00–10.75) | 4.5 (3.00–7.25) | 0.005 |
Values are presented as number (%) or median (interquartile range).
HFNC: high-flow nasal cannula; LFOS: low-flow oxygen system; APACHE: Acute Physiologic and Chronic Health Evaluation; ICU: intensive care unit; PaCO2: arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide; PaO2/FiO2: ratio of arterial oxygen partial pressure to fractional inspired oxygen; (A–a) DO2: alveolar–arterial oxygen difference; COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; SBT: spontaneous breathing trial.
a Fisher exact test;
b Type of respiratory failure can be classified according to each group, if it satisfies both criteria;
c Respiratory failure that was not satisfy each criterion.
| Variable | HFNC (n=84) | LFOS (n=34) | χ2 | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reintubation | ||||
| Early reintubation (in 72 hr) | 8 (9.5) | 3 (8.8) | - | 1.000a |
| Time to reintubation | 10.41 (1.51–62.37) | 5.00 (4.17–43.85) | 0.838b | |
| Reintubation in 168 hr | 15 (17.9) | 3 (8.8) | 1.528 | 0.216 |
| Time to reintubation | 69.00 (2.58–100.82) | 5.00 (4.17–43.85) | 0.260b | |
| Delayed reintubation (72–168 hr) | 7/76c (9.2) | 0/31c | - | 0.105a |
| Postextubation respiratory failure | ||||
| Hypoxia | 7 (8.3) | 4 (11.8) | - | 0.727a |
| Hypercapnia | 2 (2.4) | 3 (8.8) | - | 0.143a |
| Tachypnea | 14 (16.7) | 6 (17.6) | 0.017 | 0.898 |
| All types of respiratory failure | 21 (25.0) | 11 (32.4) | 0.662 | 0.416 |
| Clinical outcome | ||||
| Tracheostomy | 5 (6.0) | 1 (2.9) | - | 0.672a |
| In hospital mortality | 12 (14.3) | 3 (8.8) | - | 0.549a |
| Hospital day | 27.5 (16.0–49.7) | 14.50 (9.0–31.0) | - | 0.001b |
| Characteristics | Non-reintubation (n=69) | Reintubation (n=15) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male sex | 49 (71.0) | 11 (73.3) | 1.000a |
| Age (yr) | 74.0 (65.50–80.50) | 72.00 (67.00–74.00) | 0.245 |
| Height (cm) | 162.0 (158.0–170.0) | 164.50 (160.00–165.00) | 0.711 |
| Body weight (kg) | 58.0 (50.0–70.0) | 55.30 (50.00–60.00) | 0.656 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 22.7 (18.7–24.9) | 22.03 (19.59–23.44) | 0.717 |
| Underlying disease | |||
| Diabetes mellitus | 15 (21.7) | 4 (26.7) | 0.736a |
| Hypertension | 25 (36.2) | 6 (40.0) | 0.784 |
| Malignant disease | 6 (8.7) | 4 (26.7) | 0.073a |
| Chronic respiratory disease | 40 (58.0) | 7 (46.7) | 0.424 |
| Chronic heart disease | 18 (26.1) | 4 (26.7) | 1.000a |
| Chronic liver disease | 1 (1.4) | 0 | 1.000a |
| Chronic renal disease | 7 (10.1) | 4 (26.7) | 0.102a |
| Neurologic disease | 20 (29.0) | 7 (46.7) | 0.226a |
| Cause of mechanical ventilation | |||
| Pneumonia | 36 (52.2) | 9 (60.0) | 0.776 |
| Airway disease | 9 (13.0) | 4 (26.7) | 0.235a |
| Hemoptysis | 3 (4.3) | 0 | 1.000a |
| Drug intoxication | 13 (18.8) | 1 (6.7) | 0.447a |
| Post operation | 2 (2.9) | 0 | 1.000a |
| Heat failure | 3 (4.3) | 0 | 1.000a |
| Others | 3 (4.3) | 1 (6.7) | 0.552a |
| Type of respiratory failure at intubationb | |||
| Tachypneic respiratory failure | 5 (7.2) | 1 (6.7) | 1.000a |
| Hypercapnic respiratory failure | 31 (44.9) | 7 (46.7) | 0.902 |
| Hypoxic respiratory failure | 22 (31.9) | 1 (6.7) | 0.058a |
| Othersc | 15 (21.7) | 7 (46.7) | 0.058a |
| Severity index | |||
| APACHE II score at ICU admission | 22.0 (17.50–25.00) | 22.00 (19.00–25.00) | 0.516 |
| APACHE II score at extubation | 17.0 (15.0–19.0) | 16.00 (13.00–22.00) | 0.541 |
| Vital sign and arterial blood gas before intubation | |||
| Heart rate | 100.00 (84.00–124.50) | 101.00 (88.00–118.00) | 0.820 |
| Respiratory rate | 22.00 (18.00–26.00) | 22.00 (18.00–28.00) | 0.977 |
| PaCO2 (mmHg) | 44.90 (30.50–60.95) | 38.60 (32.00–86.00) | 0.356 |
| PaO2/FiO2 (mmHg) | 131.97 (86.90–256.19) | 120.86 (80.12–291.90) | 0.907 |
| (A–a) DO2 | 186.97 (48.71–411.96) | 179.53 (50.43- 465.58) | 0.532 |
| Vital sign and arterial blood gas before extubation | |||
| Heart rate on ventilation | 82.00 (73.50–101.00) | 87.00 (76.00–109.00) | 0.272 |
| Respiratory rate on ventilation | 18.00 (16.00–21.00) | 18.00 (15.00–20.00) | 0.366 |
| PaCO2 on ventilation (mmHg) | 34.60 (30.50–40.30) | 35.40 (27.70–46.80) | 0.717 |
| PaO2/FiO2 on ventilation (mmHg) | 286.75 (215.62–361.00) | 321.00 (165.75–400.00) | 0.939 |
| (A–a) DO2 at spontaneous breathing trial | 143.62 (110.02–166.10) | 123.42 (92.25–178.92) | 0.640 |
| High risk patient | |||
| Age older than 65 years | 53 (76.8) | 12 (80.0) | 1.000a |
| Body mass index higher than 30 kg/m2 | 6 (8.7) | 1 (6.7) | 1.000a |
| Ventilator duration more than 7 days | 22 (31.9) | 8 (53.3) | 0.116 |
| Charlson comorbidity index of 2 or more | 26 (37.7) | 7 (46.7) | 0.518a |
| APACHE II score of more than 12 | 66 (95.7) | 14 (93.3) | 0.552a |
| Heart failure as a cause of intubation | 3 (4.3) | 0 | 1.000a |
| Moderate to severe COPD | 15 (21.7) | 1 (6.7) | 0.282a |
| Failure with first SBT trial | 40 (58.0) | 12 (80.0) | 0.111 |
| Duration of mechanical ventilation before extubation (hr) | 117.15 (70.71–210.29) | 181.46 (82.83–273.66) | 0.197 |
| Hospital day before extubation trial (day) | 6.00 (4.00–10.00) | 9.00 (8.00–14.00) | 0.036 |
Values are presented as number (%) or median (interquartile range).
HFNC: high-flow nasal cannula; APACHE: Acute Physiologic and Chronic Health Evaluation; ICU: intensive care unit; PaCO2: arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide; PaO2/FiO2: ratio of arterial oxygen partial pressure to fractional inspired oxygen; (A–a) DO2: alveolar–arterial oxygen difference; COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; SBT: spontaneous breathing trial.
a Fisher exact test;
b Type of respiratory failure can be classified according to each group, if it satisfies both criteria;
c Respiratory failure that was not satisfy each criterion.
| Study | Study’s characteristics | Patient’s characteristics | Control | Reintubation | PERF | Physiologic aspect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Futier et al. [13] | Prospective RCT | Surgical patient after major abdominal surgery | LFOS | No difference | No difference | - |
| Dhillon et al. [16] | Retrospective | Critically ill surgical patient | LFOS | No differencea | - | - |
| Yu et al. [14] | Prospective RCT | Surgical patient after thoracoscopic lobectomy | LFOS | Less reintubation in HFNC | Less hypoxemic respiratory failure in HFNC | Better oxygenation, reduction of respiratory rate in HFNC |
| Hernández et al. [6] | Prospective RCT | High risk | NIV | Not inferior in HFNC | Not inferior in HFNC | No difference |
| Yoo et al. [5] | Retrospective | Mixed risk | NIV | No difference | - | - |
| Maggiore et al. [3] | Prospective RCT | Mixed risk | LFOSb | Less reintubation in HFNC | Less PERF in HFNC | Better oxygenation, reduction of respiratory rate in HFNC |
| Hernández et al. [4] | Prospective RCT | Low risk | LFOS | Less reintubation in HFNC | Less PERF in HFNC | No difference |
| Fernandez et al. [12] | Prospective RCT | Mixed risk, but include only hypercapnic patient | LFOS | No difference | No difference | - |
| Song et al. [15] | Prospective RCT | Mixed risk | LFOS | No difference | - | Better oxygenation, reduction of respiratory rate in HFNC |
| This study | Retrospective | High risk | LFOS | No difference | No difference | No differencec |
HFNC: high-flow nasal cannula; PERF: postextubation respiratory failure; RCT: randomized controlled trial; LFOS: low-flow oxygen system; NIV: noninvasive ventilation.
a In multivariable analysis, HFNC is associated with a lower risk of reintubation;
b This study only used the venturi mask as LFOS;
c In this study, HFNC shows stabilization of the heart rate after extubation.
- 1. Epstein SK. Decision to extubate. Intensive Care Med 2002;28:535-46.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Nava S, Gregoretti C, Fanfulla F, Squadrone E, Grassi M, Carlucci A, et al. Noninvasive ventilation to prevent respiratory failure after extubation in high-risk patients. Crit Care Med 2005;33:2465-70.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Maggiore SM, Idone FA, Vaschetto R, Festa R, Cataldo A, Antonicelli F, et al. Nasal high-flow versus venturi mask oxygen therapy after extubation: effects on oxygenation, comfort, and clinical outcome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2014;190:282-8.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Hernández G, Vaquero C, González P, Subira C, Frutos-Vivar F, Rialp G, et al. Effect of postextubation high-flow nasal cannula vs conventional oxygen therapy on reintubation in lowrisk patients: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2016;315:1354-61.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Yoo JW, Synn A, Huh JW, Hong SB, Koh Y, Lim CM. Clinical efficacy of high-flow nasal cannula compared to noninvasive ventilation in patients with post-extubation respiratory failure. Korean J Intern Med 2016;31:82-8.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 6. Hernández G, Vaquero C, Colinas L, Cuena R, González P, Canabal A, et al. Effect of postextubation high-flow nasal cannula vs noninvasive ventilation on reintubation and postextubation respiratory failure in high-risk patients: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2016;316:1565-74.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Ornico SR, Lobo SM, Sanches HS, Deberaldini M, Tófoli LT, Vidal AM, et al. Noninvasive ventilation immediately after extubation improves weaning outcome after acute respiratory failure: a randomized controlled trial. Crit Care 2013;17:R39. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 8. Carron M, Freo U, BaHammam AS, Dellweg D, Guarracino F, Cosentini R, et al. Complications of non-invasive ventilation techniques: a comprehensive qualitative review of randomized trials. Br J Anaesth 2013;110:896-914.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 9. Nishimura M. High-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy in adults. J Intensive Care 2015;3:15. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 10. Fricke K, Tatkov S, Domanski U, Franke KJ, Nilius G, Schneider H. Nasal high flow reduces hypercapnia by clearance of anatomical dead space in a COPD patient. Respir Med Case Rep 2016;19:115-7.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 11. Frizzola M, Miller TL, Rodriguez ME, Zhu Y, Rojas J, Hesek A, et al. High-flow nasal cannula: impact on oxygenation and ventilation in an acute lung injury model. Pediatr Pulmonol 2011;46:67-74.ArticlePubMed
- 12. Fernandez R, Subira C, Frutos-Vivar F, Rialp G, Laborda C, Masclans JR, et al. High-flow nasal cannula to prevent postextubation respiratory failure in high-risk non-hypercapnic patients: a randomized multicenter trial. Ann Intensive Care 2017;7:47. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 13. Futier E, Paugam-Burtz C, Godet T, Khoy-Ear L, Rozencwajg S, Delay JM, et al. Effect of early postextubation high-flow nasal cannula vs conventional oxygen therapy on hypoxaemia in patients after major abdominal surgery: a French multicentre randomised controlled trial (OPERA). Intensive Care Med 2016;42:1888-98.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 14. Yu Y, Qian X, Liu C, Zhu C. Effect of high-flow nasal cannula versus conventional oxygen therapy for patients with thoracoscopic lobectomy after extubation. Can Respir J 2017;2017:7894631. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 15. Song HZ, Gu JX, Xiu HQ, Cui W, Zhang GS. The value of highflow nasal cannula oxygen therapy after extubation in patients with acute respiratory failure. Clinics 2017;72:562-7.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 16. Dhillon NK, Smith EJT, Ko A, Harada MY, Polevoi D, Liang R, et al. Extubation to high-flow nasal cannula in critically ill surgical patients. J Surg Res 2017;217:258-64.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Huang HW, Sun XM, Shi ZH, Chen GQ, Chen L, Friedrich JO, et al. Effect of high-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy versus conventional oxygen therapy and noninvasive ventilation on reintubation rate in adult patients after extubation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Intensive Care Med 2018;33:609-23.ArticlePubMed
- 18. Ni YN, Luo J, Yu H, Liu D, Liang BM, Yao R, et al. Can high-flow nasal cannula reduce the rate of reintubation in adult patients after extubation? A meta-analysis. BMC Pulm Med 2017;17:142. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 19. Vallverdú I, Calaf N, Subirana M, Net A, Benito S, Mancebo J. Clinical characteristics, respiratory functional parameters, and outcome of a two-hour T-piece trial in patients weaning from mechanical ventilation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998;158:1855-62.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Lee KH, Hui KP, Chan TB, Tan WC, Lim TK. Rapid shallow breathing (frequency-tidal volume ratio) did not predict extubation outcome. Chest 1994;105:540-3.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Rittayamai N, Tscheikuna J, Rujiwit P. High-flow nasal cannula versus conventional oxygen therapy after endotracheal extubation: a randomized crossover physiologic study. Respir Care 2014;59:485-90.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Frat JP, Thille AW, Mercat A, Girault C, Ragot S, Perbet S, et al. High-flow oxygen through nasal cannula in acute hypoxemic respiratory failure. N Engl J Med 2015;372:2185-96.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Jeong ES, Lee K. Clinical application of modified burns wean assessment program scores at first spontaneous breathing trial in weaning patients from mechanical ventilation. Acute Crit Care 2018;33:260-8.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
References
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- High-flow nasal oxygen therapy compared with conventional oxygen therapy in hospitalised patients with respiratory illness: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Daniel Seow, Yet H Khor, Su-Wei Khung, David M Smallwood, Yvonne Ng, Amy Pascoe, Natasha Smallwood
BMJ Open Respiratory Research.2024; 11(1): e002342. CrossRef - Predictors and outcomes of high-flow nasal cannula failure following
extubation: A multicentre observational study
Amit Kansal, Shekhar Dhanvijay, Andrew Li, Jason Phua, Matthew Edward Cove, Wei Jun Dan Ong, Ser Hon Puah, Vicky Ng, Qiao Li Tan, Julipie Sumampong Manalansan, Michael Sharey Nocon Zamora, Michael Camba Vidanes, Juliet Tolentino Sahagun, Juvel Taculod, Ad
Annals of the Academy of Medicine, Singapore.2021; 50(6): 467. CrossRef - Flow Field Analysis of Adult High-Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy
Jingen Xia, Jiaqi Chang, Jixiang Liang, Yixuan Wang, Na Wang, Bo Xiao
Complexity.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef

 KSCCM
KSCCM
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite



