Abstract
- Transient splenial lesion of the corpus callosum can be observed in various diseases such as cancer, drug use, metabolic disorders, and cerebrovascular disorders, as well as in patients with infectious diseases. During the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, there were increasing reports of these lesions being detected on brain imaging tests performed in patients with neurological symptoms. On brain magnetic resonance imaging, findings suggestive of cytotoxic edema are observed in the splenium; these are known to disappear with improvement of clinical symptoms. Cytokinopathy caused by infection increases the permeability of the blood–brain barrier and activates the glial cells of the brain to induce cytotoxic edema. Most patients have a good prognosis. The causes, mechanism, diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of transient splenial lesions of the corpus callosum will be summarized in this review.
-
Keywords: corpus callosum; COVID-19; infections; magnetic resonance imaging
INTRODUCTION
The corpus callosum is a thick bundle of nerve fibers connecting both the cerebral hemispheres. The splenium is located in the posterior part of the corpus callosum and contains crossing axonal fibers from the occipito-parietal and temporal cortex [1,2]. Transient lesions of the splenium are reported in a variety of cytotoxic lesions of the corpus callosum (CLOCC), including mild encephalitis/encephalopathy with a reversible isolated SCC lesion (Middle East respiratory syndrome [MERS]), and reversible splenial lesion syndrome (RESLES) [3-5]. Lesions in the splenium of the corpus callosum are associated with various diseases, including infection, metabolic disturbance, drug use, epilepsy, malignancies, cerebrovascular disease, and trauma [6-10]. Recently, various neurological complications related to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) have been reported, and among them, there was a case in which a transient splenial lesion was observed [11]. In this article, we review the transient splenial lesions observed in various infectious diseases such as COVID-19.
ANATOMY, DEVELOPMENT, AND FUNCTION OF SPLENIUM
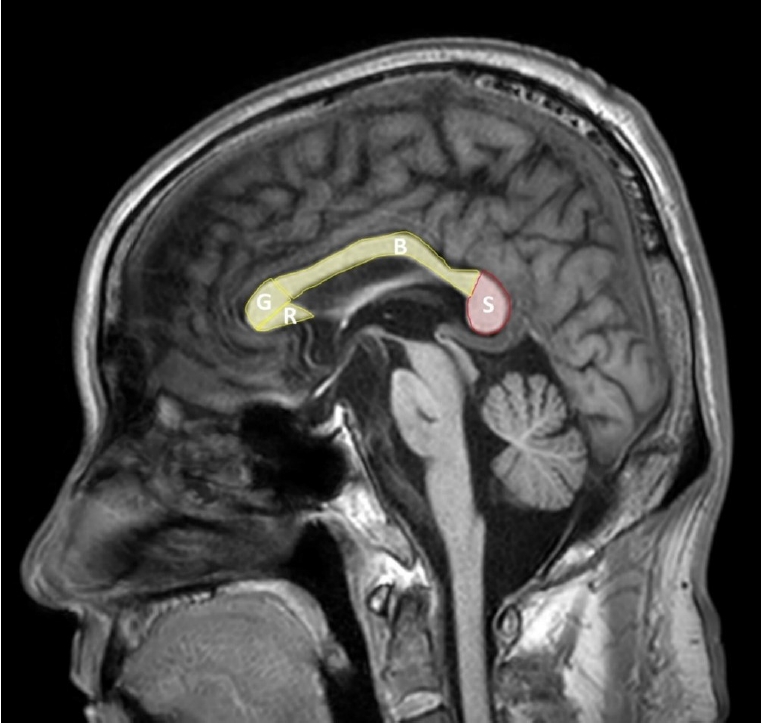
The corpus callosum is a fiber connecting the left and right cerebral hemispheres and is composed of four parts: the rostrum, genu, body, and splenium (Figure 1). Among them, the splenium contains fibers connecting the temporal and posterior parietals and the temporal cortex, during the 8th and 20th weeks of gestation period, the corpus callosum development is formed by development of the callosal precursors and complete by the age of four [12]. The internal carotid artery provides an arterial supply to most of the corpus callosum, but splenium receives blood suppls by the anterior pericallosal artery of the anterior circulation and the posterior pericallosal artery and posterior accessory pericallosal artery of the posterior circulation [1]. Splenium contains fibers connecting the temporal, parietal, and occipital cortex in both cerebral hemispheres, and thus is responsible for related functions. Callosotomy has been performed since 1940 for the treatment of epilepsy, and its function has been elucidated since then, and it is known that it is mainly related to visuospatial information transfer, language, reading and calculation, IQ, behavior and consciousness [13].
ETIOLOGY, AND INCIDENCE OF TRANSIENT SPLENIAL LESIONS
Transient splenial lesions are observed in various diseases and conditions and can be classified as follows: infectious disease, drug and toxic substance-related, metabolic disturbance, functional brain disease, malignancy, vascular disease, trauma, and miscellaneous (Table 1). According to a report published in 2011, the most common associated condition was epilepsy, followed by infection [5]. Among the recently reported cases, there are many reports related to infection, which include not only viral and bacterial infections, but also various infectious diseases such as mycoplasma, malaria, and dengue fever [14-17]. Infection-related cases are increasing, especially after the outbreak of COVID-19 [18-20]. According to a recent study, brain imaging was performed on 167 patients with neurological symptoms among 3,403 COVID-19 patients, and it was reported that splenium lesions were the most common among them [21]. The incidence of reversible splenium lesions is not precisely known, but it has been reported in several studies. In a study with 450 subjects, the prevalence was up to 3%, and in another study with 5,078 su, 30 splenial lesions were observed [22,23]. However, as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is difficult to perform in all patients, this result may be underestimated.
CLINICAL SYMPTOMS AND MANIFESTATIONS
The clinical symptoms of patients with transient splenial lesions are nonspecific and depend on the underlying disease. Many patients show symptoms that may suggest encephalopathy or encephalitis. The most common symptom is fever, which often appears as a prodromal symptom before the onset of neurological symptoms, and symptoms such as headache, vomiting, and diarrhea are also common [24]. In addition, altered mental status, seizures, confusion, behavioral change, acute urinary retention, and delirium are known common neurological symptoms. Motor deterioration, slurred speech, neck stiffness, coma, tremor, ataxia, somnolence, dysarthria, visual disturbance, and dizziness have also been reported [24-26]. However, there are cases where only a headache or fever is present without neurological symptoms [27]. Clinical symptoms of transient splenial lesions usually fully disappear within one month. Only isolated reversible lesions have a good prognosis [26]; however, patients with severe neurologic manifestations have a poor prognosis regardless of lesion improvement [27].
IMAGING FEATURES
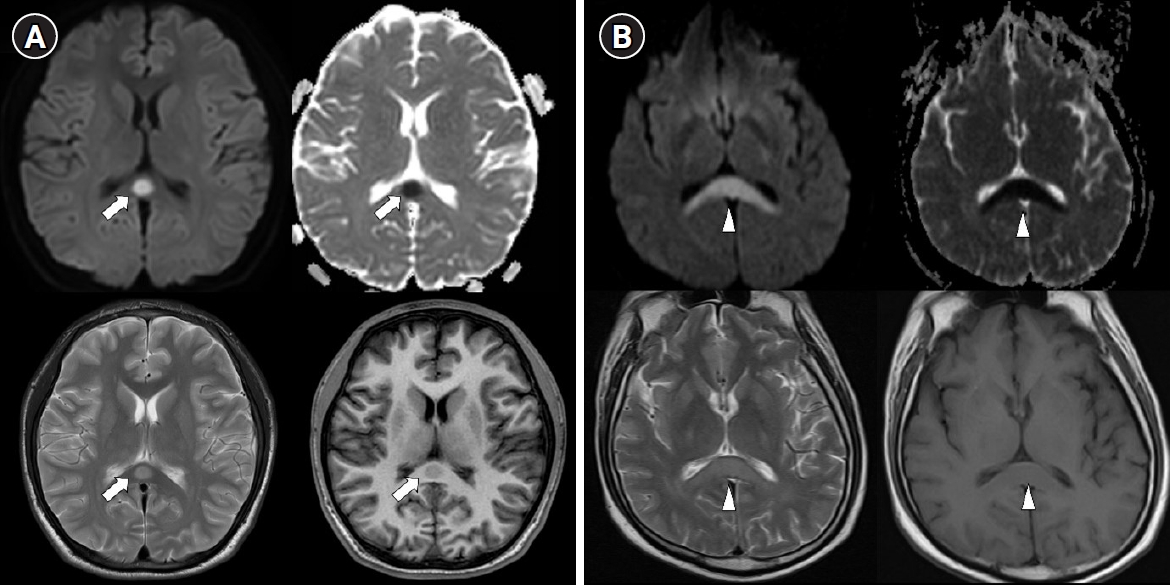
Typical MRI features are reversible hyperintense signal change on T2 weighted images, fluid-attenuated inversion recovery images, diffusion-weighted images, decreased apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values on ADC map, and hyper-isointense signals on T1-weighted images without contrast enhancement (Figure 2) [26]. Most imaging findings disappear within 2 weeks [26]. These type of MRI findings suggest cytotoxic edema, and some studies have reported that they leave neurological sequelae, but most of them disappear completely without sequelae [4]. According to the lesion type, size, and location, they are classified into two patterns as follows: (1) a small round or oval lesion, isolated in the center of splenium and (2) a lesion in the splenium expanding into the adjacent cerebral white matter or a lesion in the splenium extending into the anterior portion of the corpus callosum (the boomerang sign) [4].
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
The exact pathophysiological mechanism is not well understood. Hypotheses include intramyelinic edema, inflammatory infiltrates, hyponatremia, oxidative stress, neuroaxonal damage, autoimmune process, and cytotoxic edema [4,5,26,28-30]. When cytotoxic edema is described as a mechanism, it is sometimes referred to as “cytotoxic lesions of the corpus callosum” (or “CLOCC”) based on this [4]. When inflammatory cytokines are released they can cause overexpression of the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate, which ultimately leads to cellular swelling and cytotoxic edema due to trauma, inflammation, infection, metabolic derangement, and other associated conditions [4]. Compared with other parts of the brain, the neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes of the corpus callosum and splenium have a higher density of cytokine receptors, glutamate, and other excitatory amino acid receptors, toxin receptors, and drug receptors. Therefore, the corpus callosum and splenium may be prone to cytotoxic edema [31].
TREATMENT
Reported treatment for transient splenial lesions vary. There have been reports of immunotherapy, such as steroids and immunoglobulin, along with supportive care for the underlying disease, or treatment with prophylactic antibiotics and antivirals [24,28]. However, no differences were observed in clinical recovery and prognosis depending on the treatment method [28].
TRANSIENT SPLENIAL LESIONS AND INFECTIOUS DISEASE
Transient splenial lesions have been identified alongside various infections including viral (influenza, rotavirus, measles, adenovirus, human parvovirus B19, cytomegalovirus, varicella‐zoster, adenovirus, rubella, human herpesvirus‐6, human herpesvirus‐7, human immunodeficiency virus, mumps, parainfluenza, enterovirus, Epstein–Barr virus, Hantaan virus), bacterial (Legionella pneumophila, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Salmonella enteritidis, Escherichia coli, Enterococcus faecalis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Campylobacter jejuni), and others (Mycoplasma pneumoniae, malaria, dengue fever). Although the incidence rate in patients with infectious diseases is unknown, it is reportedly low. One study reported transient splenial lesions in 13 (1.1%) out of 1,177 children with encephalitis in a large prospective data study [24,26]. In a study of COVID-19 patients, splenial lesions were observed in three out of 73 (4.1%) COVID-19 patients who underwent MRI [31]. According to studies confirming the occurrence of brain lesions during the COVID-19 pandemic using brain imaging, macrohemorrhage or microvascular injury of subcortical white and deep white matter were observed as along with decreased diffusion of the corpus callosum [21,32,33]. Although most studies have been conducted on severely ill patients or patients with neurological symptoms, considering that there are cases found even in patients without neurological symptoms, the actual incidence of brain lesions is thought to be higher, and the incidence of transient splenial lesions are also expected to be higher. Development of viral or bacterial infectious diseases is known to induce cytotoxic edema by increasing the permeability of the blood–brain barrier and activating glial cells after infection, similar to the mechanism underlying cytotoxic edema resulting from causes other than infection [31]. However, in the case of COVID-19 patients, it was also reported that the ischemic nature may be caused by hypercoagulability [34].
CONCLUSIONS
Transient splenial lesion of the corpus callosum was previously recognized as an imaging finding of encephalitis or encephalopathy, but recently it has been reported that it can occur in various clinical situations. With the recent COVID-19 pandemic, reports of associations with viral diseases are increasing. The prognosis is good in most cases, and brain imaging can be helpful for identifying transient splenial lesions in patients who present with an infectious disease accompanied by neurological abnormalities, and can also help determine treatment and predict the prognosis of patients by differentiating stroke, etc.
KEY MESSAGES
▪ Transient splenial lesion of the corpus callosum is associated with various diseases including infections.
▪ Transient splenial lesions of the corpus callosum can be diagnosed using brain magnetic resonance imaging examination.
▪ Transient splenial lesions of the corpus callosum have also been observed in some patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
NOTES
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
Dong-Ick Shin is an editorial board member of the journal but was not involved in the peer reviewer selection, evaluation, or decision process of this article. No other potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
-
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conceptualization: all authors. Data curation: all authors. Formal analysis: all authors. Methodology: all authors. Project administration: all authors. Visualization: all authors. Writing–original draft: all authors. Writing–review & editing: all authors.
Figure 1.Sagittal view of the corpus callosum. G: genu; R: rostrum; B: body; S: splenium.
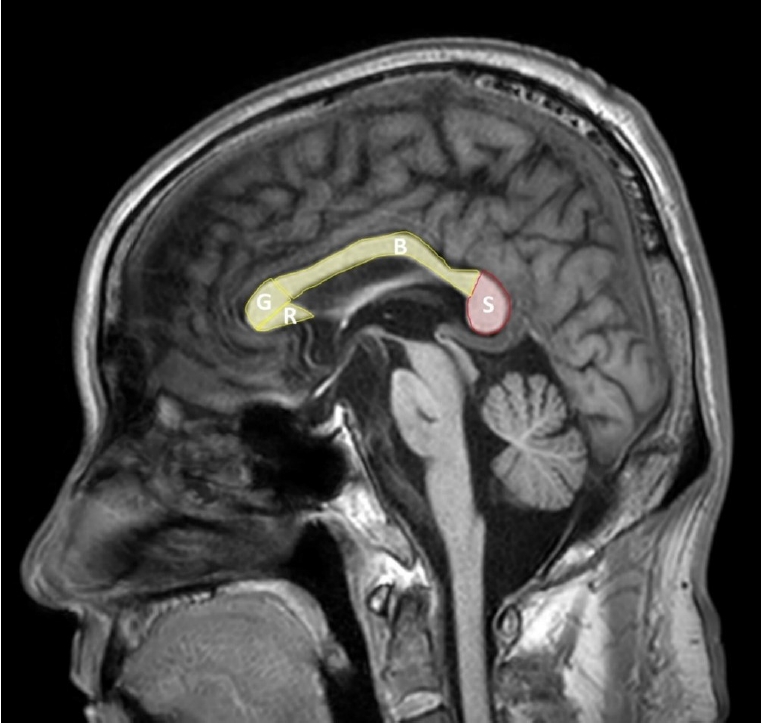
Figure 2.Two types of transient splenial lesions of the corpus callosum. Splenial lesions produce a high signal intensity on T2 diffusion-weighted imaging, a low signal intensity on T1 imaging, and decreased apparent diffusion on a coefficient map. (A) Small round lesion in the center of the splenium (arrows). (B) Boomerang sign. Lesion in the splenium extending into the adjacent cerebral white matter (arrowheads).
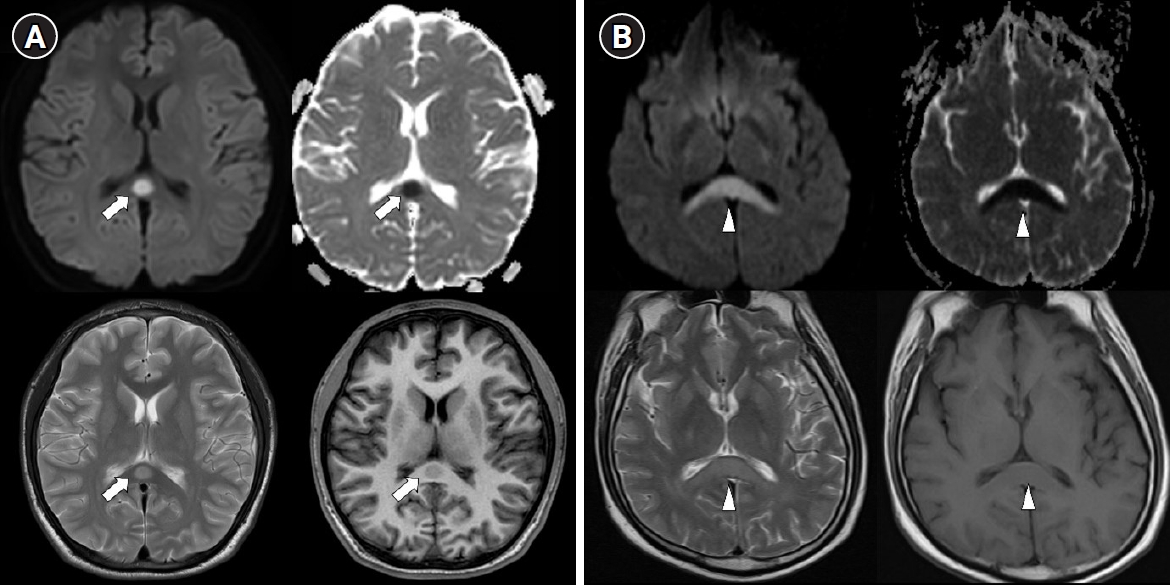
Table 1.Causative etiology of transient splenial lesion of the corpus callosum
|
Infection
|
|
|
|
Viral infection |
Bacterial infection |
Other infection |
|
Influenza |
Legionella pneumophila
|
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
|
|
Rotavirus |
Streptococcus pneumoniae
|
Malaria |
|
Measles |
Salmonella enteritidis
|
Dengue fever |
|
Adenovirus |
Escherichia coli
|
|
|
Human parvovirus B19 |
Enterococcus faecalis
|
|
|
Cytomegalovirus |
Klebsiella pneumoniae |
|
|
Varicella‐zoster |
Campylobacter jejuni
|
|
|
Adenovirus |
|
|
|
Rubella |
|
|
|
Human herpesvirus‐6 |
|
|
|
Human herpesvirus‐7 |
|
|
|
HIV |
|
|
|
Mumps |
|
|
|
Parainfluenza |
|
|
|
Enterovirus |
|
|
|
Epstein-Barr virus |
|
|
|
SARS-CoV-2 |
|
|
|
Drug related
|
|
|
|
Antiepileptic drug |
Other drug and toxic substances |
|
|
Carbamazepine |
Methyl bromide exposure |
|
|
Phenytoin |
5‐fluorouracil |
|
|
Valproate |
Cisplatin |
|
|
Lamotrigine |
Carboplatin |
|
|
Corticosteroids |
|
|
Metronidazole |
|
|
Tetracycline |
|
|
Intravenous immunoglobulin |
|
|
Alcoholism |
|
|
Carbon monoxide poisoning |
|
|
Metabolic disorder
|
|
|
|
Hypoglycemia |
|
|
|
Hypernatremia |
|
|
|
Hyponatremia |
|
|
|
Marchiafava–Bignami disease |
|
|
|
Hemolytic–uremic syndrome |
|
|
|
Thyroid storm |
|
|
|
Wernicke encephalopathy |
|
|
|
Vitamin B12 deficiency |
|
|
|
Functional brain disorder
|
|
|
|
Epilepsy |
|
|
|
Status migrainosus |
|
|
|
High‐altitude disease |
|
|
|
Transient global amnesia |
|
|
|
Malignancies
|
|
|
|
Lymphocytic leukemia |
|
|
|
Glioblastoma |
|
|
|
Spinal meningeal melanocytoma |
|
|
|
Cerebrovascular disorder or vasculitis
|
|
|
|
Subarachnoid hemorrhage |
|
|
|
Ischemic stroke |
|
|
|
Kawasaki disease |
|
|
|
Traumatic brain injury
|
|
|
|
Diffuse axonal injury |
|
|
|
Autoimmune disease
|
|
|
|
Autoimmune encephalitis |
|
|
|
N‐methyl‐d‐aspartate receptor encephalitis |
|
|
|
Autoimmune thyroid disease |
|
|
|
Anti-voltage‐gated potassium channel autoantibody syndrome |
|
|
|
Systemic lupus erythematosus |
|
|
|
Other conditions
|
|
|
|
Mumps vaccine |
|
|
|
Radiation therapy |
|
|
|
Renal failure |
|
|
|
Preeclampsia |
|
|
|
Anorexia nervosa |
|
|
|
Malnutrition |
|
|
|
Sympathomimetic‐induced kaleidoscopic visual illusion syndrome |
|
|
|
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease |
|
|
References
- 1. Knyazeva MG. Splenium of corpus callosum: patterns of interhemispheric interaction in children and adults. Neural Plast 2013;2013:639430. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 2. Raybaud C. The corpus callosum, the other great forebrain commissures, and the septum pellucidum: anatomy, development, and malformation. Neuroradiology 2010;52:447-77.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 3. Takanashi J, Hirasawa K, Tada H. Reversible restricted diffusion of entire corpus callosum. J Neurol Sci 2006;247:101-4.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Starkey J, Kobayashi N, Numaguchi Y, Moritani T. Cytotoxic lesions of the corpus callosum that show restricted diffusion: mechanisms, causes, and manifestations. Radiographics 2017;37:562-76.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Garcia-Monco JC, Cortina IE, Ferreira E, Martínez A, Ruiz L, Cabrera A, et al. Reversible splenial lesion syndrome (RESLES): what's in a name? J Neuroimaging 2011;21:e1-14.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Takanashi J, Barkovich AJ, Shiihara T, Tada H, Kawatani M, Tsukahara H, et al. Widening spectrum of a reversible splenial lesion with transiently reduced diffusion. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2006;27:836-8.PubMedPMC
- 7. Bulakbasi N, Kocaoglu M, Tayfun C, Ucoz T. Transient splenial lesion of the corpus callosum in clinically mild influenza-associated encephalitis/encephalopathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2006;27:1983-6.PubMedPMC
- 8. Singh P, Gogoi D, Vyas S, Khandelwal N. Transient splenial lesion: further experience with two cases. Indian J Radiol Imaging 2010;20:254-7.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 9. Malhotra HS, Garg RK, Vidhate MR, Sharma PK. Boomerang sign: clinical significance of transient lesion in splenium of corpus callosum. Ann Indian Acad Neurol 2012;15:151-7.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 10. Cho JS, Ha SW, Han YS, Park SE, Hong KM, Han JH, et al. Mild encephalopathy with reversible lesion in the splenium of the corpus callosum and bilateral frontal white matter. J Clin Neurol 2007;3:53-6.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 11. Kakadia B, Ahmed J, Siegal T, Jovin TG, Thon JM. Mild encephalopathy with reversible splenium lesion (MERS) in a patient with COVID-19. J Clin Neurosci 2020;79:272-4.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 12. Kahilogullari G, Comert A, Ozdemir M, Brohi RA, Ozgural O, Esmer AF, et al. Arterial vascularization patterns of the splenium: an anatomical study. Clin Anat 2013;26:675-81.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Mathews MS, Linskey ME, Binder DK, William P. Van Wagenen and the first corpus callosotomies for epilepsy. J Neurosurg 2008;108:608-13.PubMed
- 14. Lin D, Rheinboldt M. Reversible splenial lesions presenting in conjunction with febrile illness: a case series and literature review. Emerg Radiol 2017;24:599-604.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 15. Talukder NT, Feezel A, Lankford JE. Mild encephalitis/encephalopathy with a reversible splenial lesion associated with systemic Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in North America: a case report. J Med Case Rep 2022;16:74. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 16. Mawatari M, Kobayashi T, Yamamoto S, Takeshita N, Hayakawa K, Kutsuna S, et al. Mild encephalitis/encephalopathy with a reversible splenial lesion due to Plasmodium falciparum malaria: a case report. Trop Med Health 2018;46:37. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 17. Sathananthasarma P, Weeratunga PN, Chang T. Reversible splenial lesion syndrome associated with dengue fever: a case report. BMC Res Notes 2018;11:412. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 18. Varol F, Ergul N, Sahin EG, Can YY, Ergul U, Guven S, et al. Can plasma exchange therapy be an option for the treatment of SARS-CoV-2 related splenial lesion syndrome: two cases from the pediatric intensive care unit. Transfus Apher Sci 2022;103491.Article
- 19. Arıkan FA, Akdağ G, Çetiner M, Uysal N, Kabay SC. Isolated corpus callosum lesion associated with cytokine storm in COVID-19. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent) 2022;35:337-8.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 20. DE Oliveira FA, DE Melo TF, Rocha-Filho PA. Transient lesion in the splenium of the corpus callosum associated with COVID-19. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 2020;78:738. ArticlePubMed
- 21. Sawlani V, Scotton S, Nader K, Jen JP, Patel M, Gokani K, et al. COVID-19-related intracranial imaging findings: a large single-centre experience. Clin Radiol 2021;76:108-16.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 22. McLeod NA, Williams JP, Machen B, Lum GB. Normal and abnormal morphology of the corpus callosum. Neurology 1987;37:1240-2.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Park MK, Hwang SH, Jung S, Hong SS, Kwon SB. Lesions in the splenium of the corpus callosum: clinical and radiological implications. Neurol Asia 2014;19:79-88.
- 24. Chen WX, Liu HS, Yang SD, Zeng SH, Gao YY, Du ZH, et al. Reversible splenial lesion syndrome in children: retrospective study and summary of case series. Brain Dev 2016;38:915-27.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Baek SH, Shin DI, Lee HS, Lee SH, Kim HY, Shin KS, et al. Reversible splenium lesion of the corpus callosum in hemorrhagic fever with renal failure syndrome. J Korean Med Sci 2010;25:1244-6.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 26. Tada H, Takanashi J, Barkovich AJ, Oba H, Maeda M, Tsukahara H, et al. Clinically mild encephalitis/encephalopathy with a reversible splenial lesion. Neurology 2004;63:1854-8.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Doherty MJ, Jayadev S, Watson NF, Konchada RS, Hallam DK. Clinical implications of splenium magnetic resonance imaging signal changes. Arch Neurol 2005;62:433-7.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Takanashi J, Tada H, Maeda M, Suzuki M, Terada H, Barkovich AJ. Encephalopathy with a reversible splenial lesion is associated with hyponatremia. Brain Dev 2009;31:217-20.ArticlePubMed
- 29. Miyata R, Tanuma N, Hayashi M, Imamura T, Takanashi J, Nagata R, et al. Oxidative stress in patients with clinically mild encephalitis/encephalopathy with a reversible splenial lesion (MERS). Brain Dev 2012;34:124-7.ArticlePubMed
- 30. Motobayashi M, Fukuyama T, Okuno-Yuguchi J, Tsukahara K, Nagaharu S, Hagimoto R, et al. Subclinical neuroaxonal damage in patients with clinically mild encephalitis/encephalopathy with a reversible splenial lesion. Pediatr Neurol 2017;74:e3-4.ArticlePubMed
- 31. Moritani T, Smoker WR, Sato Y, Numaguchi Y, Westesson PL. Diffusion-weighted imaging of acute excitotoxic brain injury. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2005;26:216-28.PubMedPMC
- 32. Conklin J, Frosch MP, Mukerji SS, Rapalino O, Maher MD, Schaefer PW, et al. Susceptibility-weighted imaging reveals cerebral microvascular injury in severe COVID-19. J Neurol Sci 2021;421:117308. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 33. Sparr SA, Bieri PL. Infarction of the splenium of the corpus callosum in the age of COVID-19: a snapshot in time. Stroke 2020;51:e223-6.PubMed
- 34. Chougar L, Shor N, Weiss N, Galanaud D, Leclercq D, Mathon B, et al. Retrospective observational study of brain MRI findings in patients with acute SARS-CoV-2 infection and neurologic manifestations. Radiology 2020;297:E313-23.ArticlePubMedPMC
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by

- A 10-year-old girl with meningitis retention syndrome and reversible splenial lesion: A case report
Chung-Hao Wang, Chi-Nan Huang, Pei-Wei Wang
Pediatrics & Neonatology.2024; 65(2): 204. CrossRef - Legionella‐induced dysarthria and rhabdomyolysis with acute renal failure achieving recovery
Husam El Sharu, Soban Ahmad, Hunter Coore
Clinical Case Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Rickettsial infection causing non-aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage with transient corpus callosum lesion
Zahraa Noureddine El Moussaoui, Zahraa Saker, Hasan Rahhal, Ali Nasserdine, Mahmoud Younes
Journal of Medicine, Surgery, and Public Health.2024; 2: 100093. CrossRef
 , Dong-Ick Shin
, Dong-Ick Shin




 KSCCM
KSCCM

 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite