Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Acute Crit Care > Volume 39(2); 2024 > Article
-
Review Article
Pulmonary Beyond survival: understanding post-intensive care syndrome -
Lovish Gupta1
 , Maazen Naduthra Subair2
, Maazen Naduthra Subair2 , Jaskaran Munjal3
, Jaskaran Munjal3 , Bhupinder Singh4
, Bhupinder Singh4 , Vasu Bansal5
, Vasu Bansal5 , Vasu Gupta6
, Vasu Gupta6 , Rohit Jain7
, Rohit Jain7
-
Acute and Critical Care 2024;39(2):226-233.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4266/acc.2023.01158
Published online: May 24, 2024
1Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi, India
2Sri Ramachandra Institute of Higher Education and Research, Chennai, India
3Shri Ram Murti Smarak Institute of Medical Sciences, Bareilly, India
4Howard County Center for Lung and Sleep Medicine, Columbia, MD, USA
5Department of Internal Medicine, Dayanand Medical College and Hospital, Ludhiana, India
6Department of Internal Medicine, Cleveland Clinic Akron General, Akron, OH, USA
7Penn State Milton S. Hershey Medical Center, Hershey, PA, USA
- Corresponding Author: Jaskaran Munjal Shri Ram Murti Smarak Institute of Medical Sciences, Ram Murti Puram, 13 KM, Bareilly - Nainital Rd, Bhoji Pura, Abheypur Keshonpur, Uttar Pradesh 243202, India Tel: +91-20-9647-9293, Fax: +91-20-9647-9293 Email: jaskaranmunjal@gmail.com
© 2024 The Korean Society of Critical Care Medicine
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 2,270 Views
- 213 Download
Abstract
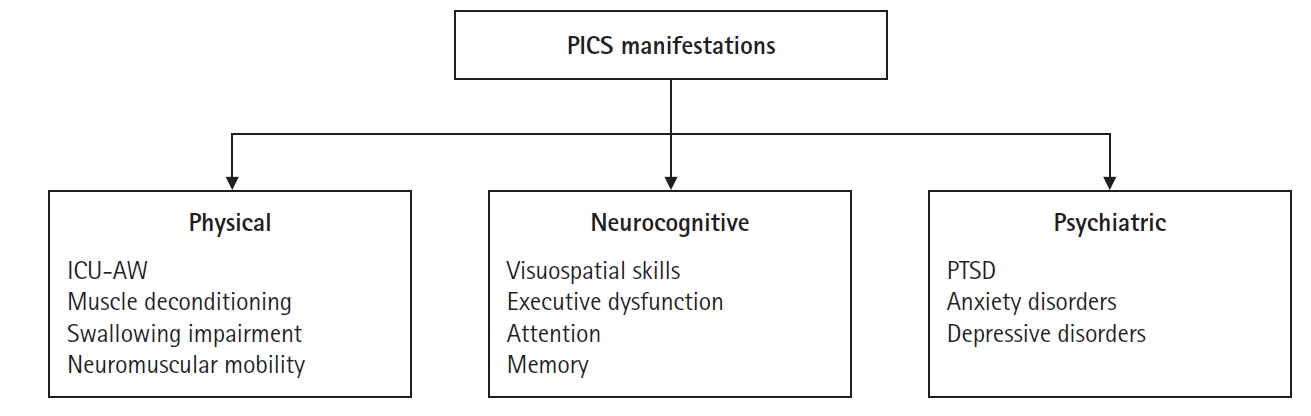
- Post-intensive care syndrome (PICS) refers to persistent or new onset physical, mental, and neurocognitive complications that can occur following a stay in the intensive care unit. PICS encompasses muscle weakness; neuropathy; cognitive deficits including memory, executive, and attention impairments; post-traumatic stress disorder; and other mood disorders. PICS can last long after hospital admission and can cause significant physical, emotional, and financial stress for patients and their families. Several modifiable risk factors, such as duration of sepsis, delirium, and mechanical ventilation, are associated with PICS. However, due to limited awareness about PICS, these factors are often overlooked. The objective of this paper is to highlight the pathophysiology, clinical features, diagnostic methods, and available preventive and treatment options for PICS.
INTRODUCTION
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
PHYSICAL IMPAIRMENTS
COGNITIVE IMPAIRMENTS
PSYCHOLOGICAL IMPAIRMENTS
DISCUSSION
CONCLUSIONS
KEY MESSAGES
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
-
FUNDING
None.
-
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
None.
-
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conceptualization: JM, BS. Visualization: JM, BS. Project administration: JM. Writing–original draft: LG, MNS, JM, BS, VB. Writing–review & editing: VB, VG, RJ.
NOTES


| Study | Drug | Use | Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bryant et al. [36] | Magnesium sulphate | Neuroprotective | Blockage of N-methyl-D-aspartate channels and voltage-gated calcium channels |
| McIntosh et al. [37] | Disodium 2,4-disulfophenyl-N-tert-butylnitrone (NXY-059) | Antioxidant effects and vascular protective properties | Free radical scavenger |
| Shuaib et al. [38] | Melatonin | Neuroprotective agent and maintenance of circadian rhythm | Alteration of catalase, glutathione peroxidase, and superoxide dismutase; and attenuation of the activation of nuclear factor-kappa B and activator protein 1 |
| Shuaib et al. [38] | Curcumin | Anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, analgesic, and hepatoprotective properties | Reduction in the expression of matrix metalloproteinases, attenuation of interleukin-1, and inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases/protein kinase C pathways |
| Panahi et al. [39] | Citicoline | Neuroprotective | Increase activity of glutathione reductase, lipid peroxidation attenuation, increase of sirtuin 1 expression |
| Hurtado et al. [40] |
- 1. Inoue S, Hatakeyama J, Kondo Y, Hifumi T, Sakuramoto H, Kawasaki T, et al. Post-intensive care syndrome: its pathophysiology, prevention, and future directions. Acute Med Surg 2019;6:233-46.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 2. Yanagi N, Kamiya K, Hamazaki N, Matsuzawa R, Nozaki K, Ichikawa T, et al. Post-intensive care syndrome as a predictor of mortality in patients with critical illness: a cohort study. PLoS One 2021;16:e0244564. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 3. Smith S, Rahman O. Postintensive care syndrome [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing. 2023;[cited 2023 Dec 1]. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32644390/.
- 4. LaBuzetta JN, Rosand J, Vranceanu AM. Review: post-intensive care syndrome: unique challenges in the neurointensive care unit. Neurocrit Care 2019;31:534-45.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 5. Renner C, Jeitziner MM, Albert M, Brinkmann S, Diserens K, Dzialowski I, et al. Guideline on multimodal rehabilitation for patients with post-intensive care syndrome. Crit Care 2023;27:301. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 6. Hiser SL, Fatima A, Ali M, Needham DM. Post-intensive care syndrome (PICS): recent updates. J Intensive Care 2023;11:23. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 7. Marra A, Pandharipande PP, Girard TD, Patel MB, Hughes CG, Jackson JC, et al. Co-occurrence of post-intensive care syndrome problems among 406 survivors of critical illness. Crit Care Med 2018;46:1393-401.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 8. Righy C, Rosa RG, da Silva RT, Kochhann R, Migliavaca CB, Robinson CC, et al. Prevalence of post-traumatic stress disorder symptoms in adult critical care survivors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care 2019;23:213. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 9. Weidman K, LaFond E, Hoffman KL, Goyal P, Parkhurst CN, Derry-Vick H, et al. Post-intensive care unit syndrome in a cohort of COVID-19 survivors in New York City. Ann Am Thorac Soc 2022;19:1158-68.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 10. Unoki T, Sakuramoto H, Uemura S, Tsujimoto T, Yamaguchi T, Shiba Y, et al. Prevalence of and risk factors for post-intensive care syndrome: multicenter study of patients living at home after treatment in 12 Japanese intensive care units, SMAP-HoPe study. PLoS One 2021;16:e0252167.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 11. Nalbandian A, Sehgal K, Gupta A, Madhavan MV, McGroder C, Stevens JS, et al. Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome. Nat Med 2021;27:601-15.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 12. Halpin SJ, McIvor C, Whyatt G, Adams A, Harvey O, McLean L, et al. Postdischarge symptoms and rehabilitation needs in survivors of COVID-19 infection: a cross-sectional evaluation. J Med Virol 2021;93:1013-22.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 13. Mulkey MA, Beacham P, McCormick MA, Everhart DE, Khan B. Minimizing post-intensive care syndrome to improve outcomes for intensive care unit survivors. Crit Care Nurse 2022;42:68-73.ArticlePMCPDF
- 14. Kress JP, Hall JB. ICU-acquired weakness and recovery from critical illness. N Engl J Med 2014;370:1626-35.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Mendelson AA, Erickson D, Villar R. The role of the microcirculation and integrative cardiovascular physiology in the pathogenesis of ICU-acquired weakness. Front Physiol 2023;14:1170429. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 16. Martín-Vicente P, López-Martínez C, Lopez-Alonso I, López-Aguilar J, Albaiceta GM, Amado-Rodríguez L. Molecular mechanisms of postintensive care syndrome. Intensive Care Med Exp 2021;9:58. PubMedPMC
- 17. Lad H, Saumur TM, Herridge MS, Dos Santos CC, Mathur S, Batt J, et al. Intensive care unit-acquired weakness: not just another muscle atrophying condition. Int J Mol Sci 2020;21:7840. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 18. Dos Santos C, Hussain SN, Mathur S, Picard M, Herridge M, Correa J, et al. Mechanisms of chronic muscle wasting and dysfunction after an intensive care unit stay: a pilot study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2016;194:821-30.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Voiriot G, Oualha M, Pierre A, Salmon-Gandonnière C, Gaudet A, Jouan Y, et al. Chronic critical illness and post-intensive care syndrome: from pathophysiology to clinical challenges. Ann Intensive Care 2022;12:58. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 20. González-López A, López-Alonso I, Aguirre A, Amado-Rodríguez L, Batalla-Solís E, Astudillo A, et al. Mechanical ventilation triggers hippocampal apoptosis by vagal and dopaminergic pathways. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2013;188:693-702.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Hughes CG, Morandi A, Girard TD, Riedel B, Thompson JL, Shintani AK, et al. Association between endothelial dysfunction and acute brain dysfunction during critical illness. Anesthesiology 2013;118:631-9.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 22. Sekino N, Selim M, Shehadah A. Sepsis-associated brain injury: underlying mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies for acute and long-term cognitive impairments. J Neuroinflammation 2022;19:101. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 23. Tokuda R, Nakamura K, Takatani Y, Tanaka C, Kondo Y, Ohbe H, et al. Sepsis-associated delirium: a narrative review. J Clin Med 2023;12:1273. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 24. Ramnarain D, Pouwels S, Fernández-Gonzalo S, Navarra-Ventura G, Balanzá-Martínez V. Delirium-related psychiatric and neurocognitive impairment and the association with post-intensive care syndrome: a narrative review. Acta Psychiatr Scand 2023;147:460-74.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 25. Wang S, Meeker JW, Perkins AJ, Gao S, Khan SH, Sigua NL, et al. Psychiatric symptoms and their association with sleep disturbances in intensive care unit survivors. Int J Gen Med 2019;12:125-30.PubMedPMC
- 26. Howard AF, Currie L, Bungay V, Meloche M, McDermid R, Crowe S, et al. Health solutions to improve post-intensive care outcomes: a realist review protocol. Syst Rev 2019;8:11. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 27. Wang S, Allen D, Kheir YN, Campbell N, Khan B. Aging and post-intensive care syndrome: a critical need for geriatric psychiatry. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 2018;26:212-21.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Sevin CM, Bloom SL, Jackson JC, Wang L, Ely EW, Stollings JL. Comprehensive care of ICU survivors: development and implementation of an ICU recovery center. J Crit Care 2018;46:141-8.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 29. Mikkelsen ME, Still M, Anderson BJ, Bienvenu OJ, Brodsky MB, Brummel N, et al. Society of Critical Care Medicine’s International Consensus Conference on prediction and identification of long-term impairments after critical illness. Crit Care Med 2020;48:1670-9.ArticlePubMed
- 30. Ahmad MH, Teo SP. Post-intensive care syndrome. Ann Geriatr Med Res 2021;25:72-8.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 31. Prescott HC, Angus DC. Enhancing recovery from sepsis: a review. JAMA 2018;319:62-75.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 32. Evans L, Rhodes A, Alhazzani W, Antonelli M, Coopersmith CM, French C, et al. Executive Summary: Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for the management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Crit Care Med 2021;49:1974-82.PubMed
- 33. Ely EW. The ABCDEF bundle: science and philosophy of how ICU liberation serves patients and families. Crit Care Med 2017;45:321-30.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 34. Rawal G, Yadav S, Kumar R. Post-intensive care syndrome: an overview. J Transl Int Med 2017;5:90-2.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 35. Garrouste-Orgeas M, Coquet I, Périer A, Timsit JF, Pochard F, Lancrin F, et al. Impact of an intensive care unit diary on psychological distress in patients and relatives. Crit Care Med 2012;40:2033-40.ArticlePubMed
- 36. Bryant SE, McNabb K. Postintensive care syndrome. Crit Care Nurs Clin North Am 2019;31:507-16.ArticlePubMed
- 37. McIntosh TK, Juhler M, Wieloch T. Novel pharmacologic strategies in the treatment of experimental traumatic brain injury: 1998. J Neurotrauma 1998;15:731-69.ArticlePubMed
- 38. Shuaib A, Lees KR, Lyden P, Grotta J, Davalos A, Davis SM, et al. NXY-059 for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 2007;357:562-71.ArticlePubMed
- 39. Panahi Y, Mojtahedzadeh M, Najafi A, Rajaee SM, Torkaman M, Sahebkar A. Neuroprotective agents in the intensive care unit: neuroprotective agents in ICU. J Pharmacopuncture 2018;21:226-40.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 40. Hurtado O, Hernández-Jiménez M, Zarruk JG, Cuartero MI, Ballesteros I, Camarero G, et al. Citicoline (CDP-choline) increases Sirtuin1 expression concomitant to neuroprotection in experimental stroke. J Neurochem 2013;126:819-26.PubMed
References
Figure & Data
References
Citations


 KSCCM
KSCCM

 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite