Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Acute Crit Care > Volume 39(2); 2024 > Article
-
Review Article
Infection Microbial infections in burn patients -
Souvik Roy1
 , Preeti Mukherjee1
, Preeti Mukherjee1 , Sutrisha Kundu1
, Sutrisha Kundu1 , Debashrita Majumder1
, Debashrita Majumder1 , Vivek Raychaudhuri1
, Vivek Raychaudhuri1 , Lopamudra Choudhury2
, Lopamudra Choudhury2
-
Acute and Critical Care 2024;39(2):214-225.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4266/acc.2023.01571
Published online: May 24, 2024
1Postgraduate and Research Department of Biotechnology, St. Xavier’s College (Autonomous), Kolkata, India
2Department of Microbiology, Sarsuna College (under Calcutta University), Kolkata, India
- Corresponding Author: Souvik Roy Postgraduate and Research Department of Biotechnology, St. Xavier’s College (Autonomous), 30, Mother Teresa Sarani, Kolkata 700016, West Bengal, India Email: souvikroybiotech@sxccal.edu
© 2024 The Korean Society of Critical Care Medicine
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 893 Views
- 94 Download
- Abstract
- INTRODUCTION
- BURN INJURIES
- EPIDEMIOLOGY OF BURN INJURIES
- ETIOLOGY OF BURN INJURIES
- PATHOGENS OF BURN WOUND INFECTIONS
- IMPACT OF GEOGRAPHICAL CONDITIONS ON THE MICROBIAL PROFILE OF BWIs
- IMPACT OF COVID-19 ON BURN INJURIES
- IMPACT OF BURN INJURIES ON THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
- INFECTION CONTROL IN BURN PATIENTS
- CONCLUSIONS
- KEY MESSAGES
- NOTES
- References
Abstract
- Polymicrobial infections are the leading causes of complications incurred from injuries that burn patients develop. Such patients admitted to the hospital have a high risk of developing hospital-acquired infections, with longer patient stays leading to increased chances of acquiring such drug-resistant infections. Acinetobacter baumannii, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Proteus mirabilis are the most common multidrug-resistant (MDR) Gram-negative bacteria identified in burn wound infections (BWIs). BWIs caused by viruses, like herpes simplex and varicella zoster, and fungi-like Candida species appear to occur occasionally. However, the preponderance of infection by opportunistic pathogens is very high in burn patients. Variations in the causative agents of BWIs are due to differences in geographic location and infection control measures. Overall, burn injuries are characterized by elevated serum cytokine levels, systemic immune response, and immunosuppression. Hence, early detection and treatment can accelerate the wound-healing process and reduce the risk of further infections at the site of injury. A multidisciplinary collaboration between burn surgeons and infectious disease specialists is also needed to properly monitor antibiotic resistance in BWI pathogens, help check the super-spread of MDR pathogens, and improve treatment outcomes as a result.
INTRODUCTION
BURN INJURIES
EPIDEMIOLOGY OF BURN INJURIES
ETIOLOGY OF BURN INJURIES
PATHOGENS OF BURN WOUND INFECTIONS
IMPACT OF GEOGRAPHICAL CONDITIONS ON THE MICROBIAL PROFILE OF BWIs
IMPACT OF COVID-19 ON BURN INJURIES
IMPACT OF BURN INJURIES ON THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
INFECTION CONTROL IN BURN PATIENTS
CONCLUSIONS
KEY MESSAGES
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
-
FUNDING
None.
-
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors express their deepest gratitude to Rev. Dr. Dominic Savio, SJ (Principal of St. Xavier’s College, Kolkata, Autonomous) and Dr. Subhankar Tripathi (Principal of Sarsuna College, Kolkata).
-
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conceptualization: SR. Data curation: PM, SK, DM, VRC. Methodology: PM, SK, DM, VRC. Writing–original draft: PM, SK, DM, VRC, Writing–review & editing: SR, LC.
NOTES


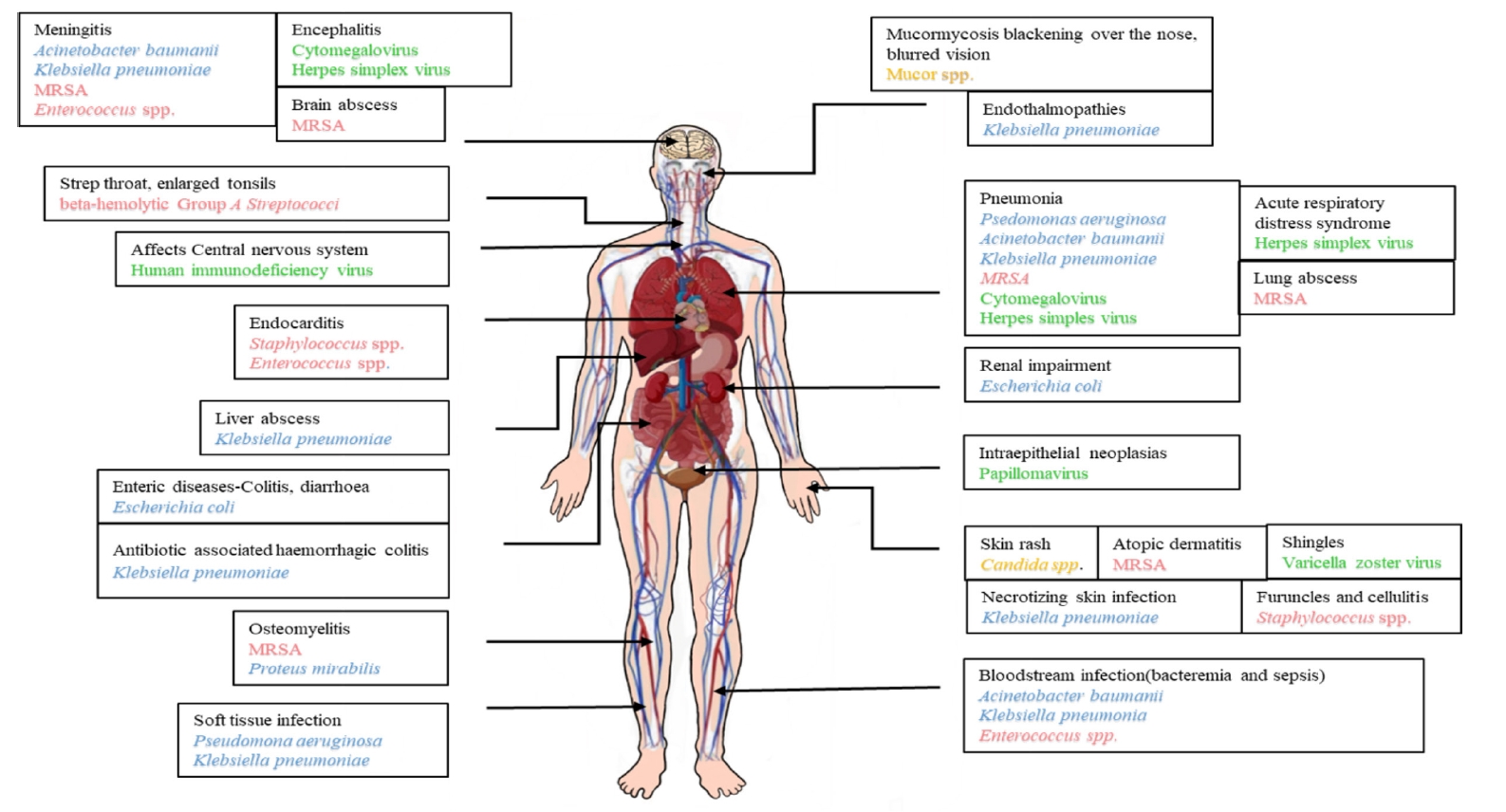
Adapted from El Hamzaoui et al. New Microbes New Infect 2020;38:100764 [15].
- 1. Mohapatra S, Gupta A, Agrawal K. Bacteriological profiles in burn patients within first twenty-four hours of injury. Int J Med Microbiol Trop Dis 2016;2:71-4.Article
- 2. Chen YY, Wu PF, Chen CS, Chen IH, Huang WT, Wang FD. Trends in microbial profile of burn patients following an event of dust explosion at a tertiary medical center. BMC Infect Dis 2020;20:193. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 3. Maslova E, Eisaiankhongi L, Sjöberg F, McCarthy RR. Burns and biofilms: priority pathogens and in vivo models. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2021;7:73. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 4. López-Jácome LE, Chávez-Heres T, Becerra-Lobato N, García-Hernández ML, Vanegas-Rodríguez ES, Colin-Castro CA, et al. Microbiology and infection profile of electric burned patients in a referral burn hospital in Mexico City. J Burn Care Res 2020;41:390-7.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 5. Forjuoh SN. Burns in low- and middle-income countries: a review of available literature on descriptive epidemiology, risk factors, treatment, and prevention. Burns 2006;32:529-37.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Peck MD. Epidemiology of burns throughout the world. Part I: distribution and risk factors. Burns 2011;37:1087-100.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Ho WS, Ying SY. An epidemiological study of 1063 hospitalized burn patients in a tertiary burns centre in Hong Kong. Burns 2001;27:119-23.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Opriessnig E, Luze H, Smolle C, Draschl A, Zrim R, Giretzlehner M, et al. Epidemiology of burn injury and the ideal dressing in global burn care: regional differences explored. Burns 2023;49:1-14.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Peck MD. Epidemiology of burns throughout the World. Part II: intentional burns in adults. Burns 2012;38:630-7.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Kara YA. Hot topics in burn injuries. Chapter 2: burn etiology and pathogenesis. Intechope. 2018.
- 11. Elsous A, Ouda M, Mohsen S, Al-Shaikh M, Mokayad S, Abo-Shaban N, et al. Epidemiology and outcomes of hospitalized burn patients in Gaza strip: a descriptive study. Ethiop J Health Sci 2016;26:9-16.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 12. Bhardwaj S, Bhatia S, Singh S, Franco F Jr. Growing emergence of drug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa and attenuation of its virulence using quorum sensing inhibitors: a critical review. Iran J Basic Med Sci 2021;24:699-719.PubMedPMC
- 13. Jeschke MG, van Baar ME, Choudhry MA, Chung KK, Gibran NS, Logsetty S. Burn injury. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2020;6:11. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 14. Norbury W, Herndon DN, Tanksley J, Jeschke MG, Finnerty CC. Infection in burns. Surg Infect (Larchmt) 2016;17:250-5.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 15. El Hamzaoui N, Barguigua A, Larouz S, Maouloua M. Epidemiology of burn wound bacterial infections at a Meknes hospital, Morocco. New Microbes New Infect 2020;38:100764. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 16. Thabet L, Messadi Aa, Mbarek M, Turki A, Meddeb B, Ben Redjeb S. Surveillance of multidrug resistant bacteria in a Tunisian hospital. Tunis Med 2008;86:992-5.PubMed
- 17. Thabet L, Turki A, Ben Redjeb S, Messadi A. Bacteriological profile and antibiotic resistance of bacteria isolates in a burn department. Tunis Med 2008;86:1051-4.ArticlePubMed
- 18. von Baum H, Ober JF, Wendt C, Wenzel RP, Edmond MB. Antibiotic-resistant bloodstream infections in hospitalized patients: specific risk factors in a high-risk population? Infection 2005;33:320-6.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 19. Wilson GR, French GW, Sully L. Loss of split thickness skin grafts due to non-group A beta-haemolytic streptococci. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 1988;70:217-9.PubMedPMC
- 20. Williams FN, Herndon DN, Hawkins HK, Lee JO, Cox RA, Kulp GA, et al. The leading causes of death after burn injury in a single pediatric burn center. Crit Care 2009;13:R183. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 21. McManus AT, Mason AD, McManus WF, Pruitt BA. Twenty-five year review of Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteremia in a burn center. Eur J Clin Microbiol 1985;4:219-23.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 22. Walton MA, Villarreal C, Herndon DN, Heggers JP. The use of aztreonam as an alternate therapy for multi-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Burns 1997;23:225-7.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Corbella X, Montero A, Pujol M, Domínguez MA, Ayats J, Argerich MJ, et al. Emergence and rapid spread of carbapenem resistance during a large and sustained hospital outbreak of multiresistant Acinetobacter baumannii. J Clin Microbiol 2000;38:4086-95.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 24. Thomas RE, Thomas BC. Reducing biofilm infections in burn patients' wounds and biofilms on surfaces in hospitals, medical facilities and medical equipment to improve burn care: a systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021;18:13195. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 25. Khan BA, Yeh AJ, Cheung GY, Otto M. Investigational therapies targeting quorum-sensing for the treatment of Staphylococcus aureus infections. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2015;24:689-704.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 26. Ramakrishnan M, Putli Bai S, Babu M. Study on biofilm formation in burn wound infection in a pediatric hospital in Chennai, India. Ann Burns Fire Disasters 2016;29:276-80.PubMedPMC
- 27. Avni T, Levcovich A, Ad-El DD, Leibovici L, Paul M. Prophylactic antibiotics for burns patients: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2010;340:c241. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 28. Falagas ME, Koletsi PK, Bliziotis IA. The diversity of definitions of multidrug-resistant (MDR) and pandrug-resistant (PDR) Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Med Microbiol 2006;55(Pt 12):1619-29.ArticlePubMed
- 29. Gupta M, Naik AK, Singh SK. Bacteriological profile and antimicrobial resistance patterns of burn wound infections in a tertiary care hospital. Heliyon 2019;5:e02956. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 30. BioMérieux. Burn patients often have higher rates of multidrug-resistant infections—but there are ways to help [Internet]. BioMérieux. 2023;[cited 2024 May 1]. Available from: https://www.biomerieux.com/nl/en/blog/antimicrobial-resistance-stewardship/Burn-Patients-Multidrug-Resistant-Infections.html.
- 31. Lachiewicz AM, Hauck CG, Weber DJ, Cairns BA, van Duin D. Bacterial infections after burn injuries: impact of multidrug resistance. Clin Infect Dis 2017;65:2130-6.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 32. Wanis M, Walker SA, Daneman N, Elligsen M, Palmay L, Simor A, et al. Impact of hospital length of stay on the distribution of Gram negative bacteria and likelihood of isolating a resistant organism in a Canadian burn center. Burns 2016;42:104-11.ArticlePubMed
- 33. Sheridan R, Weber J, Chang P. Multi-drug resistant Gram-negative bacteria colonization and infection in burned children: lessons learned from a 20-year experience. Burns Open 2018;2:43-6.Article
- 34. Rosanova MT, Stamboulian D, Lede R. Risk factors for mortality in burn children. Braz J Infect Dis 2014;18:144-9.ArticlePubMed
- 35. Taneja N, Emmanuel R, Chari PS, Sharma M. A prospective study of hospital-acquired infections in burn patients at a tertiary care referral centre in North India. Burns 2004;30:665-9.ArticlePubMed
- 36. Kabanangi F, Joachim A, Nkuwi EJ, Manyahi J, Moyo S, Majigo M. High level of multidrug-resistant gram-negative pathogens causing burn wound infections in hospitalized children in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. Int J Microbiol 2021;2021:6644185. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 37. Magiorakos AP, Srinivasan A, Carey RB, Carmeli Y, Falagas ME, Giske CG, et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: an international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin Microbiol Infect 2012;18:268-81.ArticlePubMed
- 38. Gupta N, Haque A, Lattif AA, Narayan RP, Mukhopadhyay G, Prasad R. Epidemiology and molecular typing of Candida isolates from burn patients. Mycopathologia 2004;158:397-405.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 39. Horvath EE, Murray CK, Vaughan GM, Chung KK, Hospenthal DR, Wade CE, et al. Fungal wound infection (not colonization) is independently associated with mortality in burn patients. Ann Surg 2007;245:978-85.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 40. Mousa HA. Fungal infection of burn wounds in patients with open and occlusive treatment methods. East Mediterr Health J 1999;5:333-6.ArticlePubMed
- 41. Ahmad S, Khan Z, Mustafa AS, Khan ZU. Epidemiology of Candida colonization in an intensive care unit of a teaching hospital in Kuwait. Med Mycol 2003;41:487-93.ArticlePubMed
- 42. Murray CK, Loo FL, Hospenthal DR, Cancio LC, Jones JA, Kim SH, et al. Incidence of systemic fungal infection and related mortality following severe burns. Burns 2008;34:1108-12.ArticlePubMed
- 43. Becker WK, Cioffi WG, McManus AT, Kim SH, McManus WF, Mason AD, et al. Fungal burn wound infection: a 10-year experience. Arch Surg 1991;126:44-8.ArticlePubMed
- 44. Ballard J, Edelman L, Saffle J, Sheridan R, Kagan R, Bracco D, et al. Positive fungal cultures in burn patients: a multicenter review. J Burn Care Res 2008;29:213-21.ArticlePubMed
- 45. Greenhalgh DG, Saffle JR, Holmes JH, Gamelli RL, Palmieri TL, Horton JW, et al. American Burn Association consensus conference to define sepsis and infection in burns. J Burn Care Res 2007;28:776-90.ArticlePubMed
- 46. Mathew BP, Nath M. Recent approaches to antifungal therapy for invasive mycoses. ChemMedChem 2009;4:310-23.ArticlePubMed
- 47. Dries DJ. Management of burn injuries: recent developments in resuscitation, infection control and outcomes research. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med 2009;17:14. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 48. Struck MF. Infection control in burn patients: are fungal infections underestimated? Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med 2009;17:51-6.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 49. de Macedo JL, Santos JB. Bacterial and fungal colonization of burn wounds. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 2005;100:535-9.ArticlePubMed
- 50. Church D, Elsayed S, Reid O, Winston B, Lindsay R. Burn wound infections. Clin Microbiol Rev 2006;19:403-34.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 51. Capoor MR, Sarabahi S, Tiwari VK, Narayanan RP. Fungal infections in burns: diagnosis and management. Indian J Plast Surg 2010;43(Suppl):S37-42.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 52. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Reference method for broth dilution antifungal susceptibility testing of yeasts; approved standard. Second edition. NCCLS document M27-A2 [ISBN 1-56238-469-4] [Internet]. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. 2002;[cited 2024 May 1]. Available from: https://webstore.ansi.org/preview-pages/CLSI/preview_M27-A2.pdf.
- 53. Mousa HA. Aerobic, anaerobic and fungal burn wound infections. J Hosp Infect 1997;37:317-23.ArticlePubMed
- 54. Baj J, Korona-Głowniak I, Buszewicz G, Forma A, Sitarz M, Teresiński G. Viral infections in burn patients: a state-of-the-art review. Viruses 2020;12:1315. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 55. Xu H, Su C, Pearson A, Mody CH, Zheng C. Herpes simplex virus 1 UL24 abrogates the DNA sensing signal pathway by inhibiting NF-κB activation. J Virol 2017;91:e00025-17.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 56. Wood JJ, O'Mahony JB, Rodrick ML, Eaton R, Demling RH, Mannick JA. Abnormalities of antibody production after thermal injury: an association with reduced interleukin 2 production. Arch Surg 1986;121:108-15.ArticlePubMed
- 57. Haik J, Weissman O, Stavrou D, Ben-noon HI, Liran A, Tessone A, et al. Is prophylactic acyclovir treatment warranted for prevention of herpes simplex virus infections in facial burns? A review of the literature. J Burn Care Res 2011;32:358-62.ArticlePubMed
- 58. Rennekampff HO, Hamprecht K. Cytomegalovirus infection in burns: a review. J Med Microbiol 2006;55:483-7.ArticlePubMed
- 59. Schwacha MG. Macrophages and post-burn immune dysfunction. Burns 2003;29:1-14.ArticlePubMed
- 60. Bordes J, Maslin J, Prunet B, d'Aranda E, Lacroix G, Goutorbe P, et al. Cytomegalovirus infection in severe burn patients monitoring by real-time polymerase chain reaction: a prospective study. Burns 2011;37:434-9.ArticlePubMed
- 61. Wurzer P, Guillory A, Parvizi D, Clayton RP, Branski LK, Kamolz LP, et al. Human herpes viruses in burn patients: a systematic review. Burns 2017;43:25-33.ArticlePubMed
- 62. Sheridan RL, Weber JM, Pasternak MM, Mulligan JM, Tompkins RG. A 15-year experience with varicella infections in a pediatric burn unit. Burns 1999;25:353-6.ArticlePubMed
- 63. Midilli K, Erkiliç A, Kuşkucu M, Analay H, Erkiliç S, Benzonana N, et al. Nosocomial outbreak of disseminated orf infection in a burn unit, Gaziantep, Turkey, October to December 2012. Euro Surveill 2013;18:20425. ArticlePubMed
- 64. Bergqvist C, Kurban M, Abbas O. Orf virus infection. Rev Med Virol 2017;27.ArticlePDF
- 65. Al-Qattan MM. Orf infection of the hand. J Hand Surg Am 2011;36:1855-8.ArticlePubMed
- 66. Edge JM, Van der Merwe AE, Pieper CH, Bouic P. Clinical outcome of HIV positive patients with moderate to severe burns. Burns 2001;27:111-4.ArticlePubMed
- 67. Allgöwer M, Schoenenberger GA, Sparkes BG. Burning the largest immune organ. Burns 1995;21 Suppl 1:S7-47.PubMed
- 68. Camilleri IG, Milner RH. Human papilloma virus proliferation in a healing burn. Burns 1996;22:162-3.ArticlePubMed
- 69. Espinoza LF, Friedstat J, Faoro N, Chang PH, McMullen KA, Simko LC, et al. Geographic variation in outcomes after burn injury: a burn model system national database study. Ann Plast Surg 2020;84:644-50.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 70. Gupta VK, Paul S, Dutta C. Geography, ethnicity or subsistence-specific variations in human microbiome composition and diversity. Front Microbiol 2017;8:1162. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 71. Ozumba UC, Jiburum BC. Bacteriology of burn wounds in Enugu, Nigeria. Burns 2000;26:178-80.ArticlePubMed
- 72. Laura P, José A, Nikki A, Khaled A, Barret J, Jeffery C, et al. Impact of COVID-19 on global burn care. Burns 2022;48:1301-10.ArticlePubMed
- 73. Sierawska O, Małkowska P, Taskin C, Hrynkiewicz R, Mertowska P, Grywalska E, et al. Innate immune system response to burn damage-focus on cytokine alteration. Int J Mol Sci 2022;23:716. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 74. Vinish M, Cui W, Stafford E, Bae L, Hawkins H, Cox R, et al. Dendritic cells modulate burn wound healing by enhancing early proliferation. Wound Repair Regen 2016;24:6-13.ArticlePubMed
- 75. Rani M, Schwacha MG. Aging and the pathogenic response to burn. Aging Dis 2012;3:171-80.PubMed
- 76. Grogan JB. Altered neutrophil phagocytic function in burn patients. J Trauma 1976;16:734-8.ArticlePubMed
- 77. Rich RR. Clinical immunology principles and practices. 2001, Mosby.
- 78. Altman LC, Furukawa CT, Klebanoff SJ. Depressed mononuclear leukocyte chemotaxis in thermally injured patients. J Immunol 1977;119:199-205.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 79. Moins-Teisserenc H, Cordeiro DJ, Audigier V, Ressaire Q, Benyamina M, Lambert J, et al. Severe altered immune status after burn injury is associated with bacterial infection and septic shock. Front Immunol 2021;12:586195. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 80. Coban YK. Infection control in severely burned patients. World J Crit Care Med 2012;1:94-101.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 81. Boyce JM, White RL, Causey WA, Lockwood WR. Burn units as a source of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections. JAMA 1983;249:2803-7.ArticlePubMed
- 82. Wolvos T. Wound instillation: the next step in negative pressure wound therapy. Lessons learned from initial experiences. Ostomy Wound Manage 2004;50:56-66.
- 83. Wilson JR, Mills JG, Prather ID, Dimitrijevich SD. A toxicity index of skin and wound cleansers used on in vitro fibroblasts and keratinocytes. Adv Skin Wound Care 2005;18:373-8.ArticlePubMed
- 84. Coban YK, Erkiliç A, Analay H. Our 18-month experience at a new burn center in Gaziantep, Turkey. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2010;16:353-6.PubMed
References
Figure & Data
References
Citations


 KSCCM
KSCCM
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite