Abstract
-
Background
- We assessed predictors of mortality in the intensive care unit (ICU) and investigated if Glasgow coma scale (GCS) is associated with mortality in patients undergoing endotracheal intubation (EI).
-
Methods
- From February 2020, we performed a 1-year study on 2,055 adult patients admitted to the ICU of two teaching hospitals. The outcome was mortality during ICU stay and the predictors were patients’ demographic, clinical, and laboratory features.
-
Results
- EI was associated with a decreased risk for mortality compared with similar patients (adjusted odds ratio [AOR], 0.32; P=0.030). This shows that EI had been performed correctly with proper indications. Increasing age (AOR, 1.04; P<0.001) or blood pressure (AOR, 1.01; P<0.001), respiratory problems (AOR, 3.24; P<0.001), nosocomial infection (AOR, 1.64; P=0.014), diabetes (AOR, 5.69; P<0.001), history of myocardial infarction (AOR, 2.52; P<0.001), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (AOR, 3.93; P<0.001), immunosuppression (AOR, 3.15; P<0.001), and the use of anesthetics/sedatives/hypnotics for reasons other than EI (AOR, 4.60; P<0.001) were directly; and GCS (AOR, 0.84; P<0.001) was inversely related to mortality. In patients with trauma surgeries (AOR, 0.62; P=0.014) or other surgical categories (AOR, 0.61; P=0.024) undergoing EI, GCS had an inverse relation with mortality (accuracy=82.6%, area under the receiver operator characteristic curve=0.81).
-
Conclusions
- A variety of features affected the risk for mortality in patients admitted to the ICU. Considering GCS score for EI had the potential of affecting prognosis in subgroups of patients such as those with trauma surgeries or other surgical categories.
-
Keywords: endotracheal intubation; Glasgow coma scale; intensive care unit; logistic models; mortality; risk factors
INTRODUCTION
Endotracheal intubation (EI) for oxygenation, ventilation, and airway protection is carried out for advanced airway management particularly in trauma patients [1]. However, the potential risks associated with the procedure have led to some controversies regarding the indications and timing of EI [1-4]. Patients with decreased consciousness are frequently candidates for EI. The American College of Surgeons Committee on Trauma and the Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma recommended EI for patients with a Glasgow coma scale (GCS) of 8 or lower [1,5]. Later, the Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma added the GCS of 9–12 as a level 3 recommendation for EI [6]. A review study suggested that EI has been commonly carried out in patients with altered mental status (GCS >8) [7].
There are still uncertainties concerning the relation of GCS with EI indication. A cohort study of patients with drug or alcohol intoxication suggested that EI is not mandatory even in a GCS of 8 or less [8]. In patients with GCS of 7 or 8 and isolated head injury, immediate EI was reported to be associated with higher mortality risk, while it was recommended for blunt head injury patients younger than 45 years and a GCS of 7 on admission [9]. Another study suggested that EI in trauma patients with GCS of 6 to 8 on admission increased mortality and that the use of a GCS threshold to mandate EI should be revisited [1]. However, in a review of 1,000 intubations carried out in the first 2 hours after arrival at a Level I trauma center, Sise et. al [7] reported that early EI was safe and effective in trauma patients and that the Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma Guidelines might miss patients who would benefit from EI early after injury. The clinical risk or advantages of EI in medical patients with a low GCS score has not been well established yet [7,9,10].
Nevertheless, GCS is a useful scoring system for predicting mortality in the intensive care unit (ICU) [11] even in a mixed population of critically ill patients [12]. Information on the predictive ability of GCS scores aids caregivers in coordinating the healthcare team and in improving outcomes for both patient and family on admission and discharge [13,14]. However, the potential of GCS for decision-making on EI still requires careful evaluation.
The aim of conducting the present study was to assess the association of GCS with the mortality rate in subgroups of patients undergoing EI. This would help the reader to see if GCS could be of prognostic value in patients undergoing EI. We hypothesized that GCS would be associated with different EI outcomes at least in some patient categories. We also assessed predictors of mortality in the ICU to identify patients who most benefit from EI in a sample of ICU patients based on their GCS score.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Design and Setting
From February 2020 for one year we carried out a study of ICU patients. The study was conducted by the Critical Care Quality Improvement Research Center, affiliated with Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences. It was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Ethics approval was obtained from the Institutional Review Boards of AJA University of Medical Sciences (No. IR.AJAUMS.REC.1397.697696). All participants or their companions signed written consents for using patients’ data in the analyses. Patients were from two teaching hospitals affiliated with Universities of Medical Sciences. The hospitals are well-equipped settings with high patient turnovers and are large referral and subspecialty centers.
Data Collection
We included all adult patients who were admitted to the ICU. For patients with readmission within the study time period, only the first ICU admission was considered for data entry and analysis. A number of demographic, clinical, and laboratory features were recorded for each patient. Also, patients were monitored for undergoing any important procedure, and for mortality during the ICU stay. The GCS scores were determined by four study anesthesiologists and intensivists who were experts in the assessment of patients. In each work shift, a study nurse recorded the information for each patient. Data were entered into a paper form, and then, into the spreadsheet of Microsoft Office Excel software.
Outcome and Predictors
The outcome of the study was mortality during ICU stay. The predictors were primarily selected based on a consensus of the authors considering the limits of time, budget, and personnel [15,16]. We recorded patients’ sex and age, significant comorbidities, vital signs, information on nosocomial infections if any, the reason for admission, arterial blood gas, and a number of other laboratory test results, GCS on admission or immediately before EI (for patients undergoing EI), and significant procedures (including EI). All recorded variables reflected the status of patients on admission (e.g., comorbidities) or within their ICU stay (e.g., blood pressure). All patients arrive at the ICU without EI. The EI variable was recorded as a binary feature rather than numeric. Therefore, patients with re-intubation during their ICU stay were also labeled 1. Data were assessed for variables’ distribution, missing values, duplicate cases, and severe class imbalance (less than 1% frequency for any level).
Feature Selection and Modeling
We used the random forest to estimate variable importance. The random forest was used for feature selection because of its good performance, low overfitting, easy interpretability, and robustness to the presence of correlated features [17]. The data were then partitioned into development (training) and validation (test) datasets; 80, and 20%, respectively. Next, we included the selected variables into a binary logistic model and evaluated the performance of the regression. Three logistic models were developed: a base model, the second model incorporating the interaction term of EI×GCS, and the third with added EI×GCS×admission category. The strength of associations was reported using adjusted odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). The model’s fitness was assessed with chi-squared tests and the amount of variation in the dependent variables explained by the models was evaluated using Nagelkerke R2. We investigated the performance of classifiers by calculating accuracy metrics: the percentage of the correctly classified records, sensitivity, specificity, positive predicted value, F1, balanced accuracy, and area under the receiver operator characteristic. For statistical analyses, point estimates, 95% CI, and p-values were calculated. P-values less than 0.05 were considered significant. Results are presented as mean and standard deviation (SD) for continuous variables, and as absolute numbers (%) for categorical data. The means of the continuous variables were compared using independent sample t-tests. The normality of the outcome variables was examined with the Shapiro-Wilk test and the homogeneity of variances was investigated with Levene’s test. Either a chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test was used for testing differences among the study groups for categorical variables.
Software
We imported the data into R software version 4.0.2 (A language and environment for statistical computing (R Foundation for Statistical Computing; https://www.R-project.org/). R is a well-known free software environment for statistical and machine learning libraries and graphics. We used a variety of R packages for the analysis. All the packages were downloaded from the Comprehensive R Archive Network (https://cran.r-project.org/), the official R package repository, or the GitHub (https://github.com/) website.
RESULTS
Participants
Data from 2,055 patients were analyzed. There were no missing data or duplicate cases in our sample. Mean age (SD) was 55.0 years (15.6 years) and 983 patients (47.8%) were women. Overall, 865 patients (42.1%) died and 893 (43.5%) underwent EI. A GCS of 10 was used as an indication for EI with no exceptions, all patients with GCS ≤10 underwent EI, no patients with GCS >11 underwent EI (Figure 1). Table 1 shows the main characteristics of dead and alive groups of ICU patients. There were statistically significant differences between the two groups in reason for admission, nosocomial infection, surgery, diabetes, myocardial infarction, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, immunosuppression, use of anesthetics/sedatives/hypnotics for reasons other than EI, age, systolic blood pressure, and fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2) were significantly different between the two groups. Figure 2 shows the results of the feature selection. The features were sorted according to their importance to the prediction. We included the selected predictors in logistic regression models.
Model Development
We constructed three logistic models of mortality: model 1 included the selected predictors, model 2 incorporated the interaction term of EI×GCS into the model 1, and model 3 added EI×GCS×admission category to model 2. The model 1, was well-fitted to the data, χ2(19)=693.817, P<0.001, Nagelkerke R2=0.534, Hosmer and Lemeshow goodness of fit test χ2(59)=2.464, P≈1.000, Akaike's information criterion (AIC)=1,305.1. The model 2 was also well-fitted, χ2(20)=708.370, P<0.001, Nagelkerke R2=0.523, Hosmer and Lemeshow χ2(59)=13.833, p≈1.000, AIC=1,292.5. But the model 3 was the best, χ2(32)=802.848, P<0.001, Nagelkerke R2=0.575, Hosmer and Lemeshow χ2(59)=10.755, P≈1.000, AIC=1,222.1. Also, pairwise comparisons between the models showed that model 2 is not statistically different from model 1, χ2(1)=2.626, P=0.105, ∆AIC=12.6; however, model 3 is better than model 2, χ2(12)=94.479, P<0.001, ∆AIC=70.4.
Model Validation and Specification
Analysis showed a high performance for model 3; accuracy (95% CI): 82.6% (79.4%–85.5%), McNemar's test P<0.001, sensitivity=90.4%, specificity=71.8%, positive predicted value=81.6%, F1=85.8%, balanced Accuracy=81.1%, and area under the receiver operator characteristic=0.81 (Figure 3). Table 2 shows the association of predictors with mortality. Overall, EI decreased the risk for mortality in ICU patients when adjusted for other risk factors. Patients with respiratory problems, nosocomial infection, diabetes, history of myocardial infarction, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, immunosuppression, use of anesthetics/sedatives/hypnotics during ICU stay for reasons other than EI showed a greater risk for mortality. Also, death risk increased with increasing age and systolic blood pressure. In addition, GCS had plausibly an inverse relation with the risk of mortality. Of the model’s interaction terms, two were significant and two were not. The significant terms showed that in the “trauma” and “other” surgeries undergoing EI, GCS had an inverse relation with mortality compared with the reference category ("other medical problems"). However, in the “respiratory” problems and “elective brain” surgeries, patients undergoing EI did not show a significant relation between their GCS and the risk for mortality.
DISCUSSION
We assessed mortality predictors for ICU patients, and also mortality rate in subgroups of patients to see if GCS could affect the outcome of EI. Our study showed that a variety of predictors had a significant relation with ICU mortality. Patients undergoing EI had a decreased risk for mortality when adjusted for other risk factors. This does not imply that EI should be prescribed for all patients but shows that EI had been performed correctly with proper indications. Other risk factors of death were having respiratory problems, nosocomial infection, diabetes, history of myocardial infarction, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, immunosuppression, and the use of anesthetics/sedatives/hypnotics for reasons other than EI during ICU stay. A small, but statistically significant relationship was present between age or blood pressure and the risk for mortality. These relations are clinically plausible and expected. Older patients have greater illness severity and more comorbidities and therefore higher risk for mortality [18]. Patients with nosocomial infection [19,20], diabetes [21], respiratory diseases [22,23], myocardial infarction, and blood hypertension have been frequently reported to have a higher risk for ICU mortality.
Overall, many studies implied that GCS could be used as an indicator for clinical decision-making in critical patients. In a trauma quality improvement program study, Jakob et al. included patients with a GCS score of 7 or 8 and isolated head injury. They reported that immediate intubation was associated with higher mortality (OR, 1.79; 95% CI, 1.31–2.44; P<0.001) [9]. Our data of patients undergoing brain surgery suggested that there is no significant relation between EI and mortality considering GCS score. The difference may be explained as due to including different populations with different sample sizes; head trauma in their study (n=2,727) versus brain surgery in ours (n=267). Patients with head trauma are more prone to mortality than people undergoing elective brain surgery. Our study confirmed the association of age with the risk of ICU mortality reported in other studies [24]. However, our estimated OR for age was not very high.
Our study suggested that group heterogeneity should be noticed in investigating ICU patients to make clinical guidelines. Bendinelli et al. [25] included patients with traumatic brain injury in two groups of GCS 3–5 (n=99) and GCS 6–8 (n=49) and compared them in predictors of EI success. They concluded that patients with GCS <9 should be considered as heterogeneous populations. The sample size in Bendinelli’s study [25] was too small to allow subgroup analysis. Our study extended the concept of heterogeneity of patient groups to diagnostic categories and showed hidden relations with mortality in the subgroups. Studies suggested that to support the EI of patients with medical problems based on a GCS score, other factors such as disease trajectory, diagnosis, and prognosis, must be considered [10]. Again our study extended this concept to surgical patients.
Adding the interaction terms of EI×GCS and EI×GCS×admission category to our logistic models improved the performance metrics. This showed that there is a significant association between EI and GCS, and lower mortality rates. However, the specification of the final model indicated that such relations are evident in subgroups of patients. Our analysis revealed that the mortality among patients having EI and undergoing trauma surgery or a variety of surgeries other than trauma or brain surgery is associated with GCS. Nevertheless, in patients with respiratory problems or brain surgery, such a relation is not significant. This shows that the value of GCS is practically important for decision-making on EI in subgroups of ICU patients.
Conversely, research suggested that the GCS score does not provide supportive evidence for carrying out EI. In a study carried out by Hatchimonji et al. [1], the effect of EI on mortality and length of ICU stay was assessed in trauma patients with a GCS score of 6–8. They included 6,676 patients and reported increased mortality associated with EI (OR, 1.05; 95% CI, 1.03–1.06). They also reported similar results in patients with (OR, 1.04; 95% CI, 1.02–1.06) and without head injuries (OR, 1.06; 95% CI, 1.03–1.10). It was concluded that in patients with GCS of 6–8, intubation on arrival was associated with an increase in mortality and that the use of a strict threshold GCS to mandate EI should be revisited [1]. Our results were in accordance with Hatchimonji’s study [1] in patients with brain surgery and respiratory insufficiency. However, we cannot appreciate the general message of their study despite their advantage in including a large sample. They categorized patients into with and without head injuries; narrowed the range of GCS scores to 6–8; confined patients’ characteristics to a small set of predictors; and estimated a 3 to 10% increase in mortality for intubated patients. Models based on GCS still provide useful information in estimating the risk for mortality in ICU patients with specific health problems [11,26,27]. We are not trying to suggest that GCS alone should be used as a guide to EI in all ICU patients, but we suggest that considering GCS score has the potential of changing prognosis in subgroups of patients such as in trauma surgeries. Improved healthcare for individuals requires predicting certain health-related outcomes and the logistic regression for binary outcomes is a frequently used techniques for developing predictive models [28].
We assessed a large number of predictors of mortality in ICU patients. Our analyses were straightforward and the results had similarities with what has been reported in the literature. Our sample size was enough to find statistically significant large associations. However, for some predictors such as age, systolic blood pressure, and respiratory rate the results seemed statistically significant while practically unimportant. Therefore, overpowering of the statistical tests is not unlikely and the results should be interpreted cautiously. We were not able to well identify all subgroups of patients benefiting from GCS considerations in decision-making for EI. While we recognized generic categories of patients, our data were not enough to let us make recommendations for specific medical or surgical patients or to suggest specific cut-offs for GCS in all patient subgroups. We did not extend our results beyond the available data but, to assess other possible consequences of GCS guidance for decision making on EI, such as hospital stay and the long-term complications, further research with larger sample sizes is needed.
We found in our study that a variety of predictors have a significant relation with ICU mortality. Our results suggested that patients undergoing EI had a decreased risk for mortality compared with similar patients without EI. Increasing age, systolic blood pressure, respiratory problems, nosocomial infection, diabetes, history of myocardial infarction, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, immunosuppression, and the use of anesthetics/sedatives/hypnotics during ICU stay for reasons other than EI were directly associated, and GCS was inversely related to ICU mortality risk. Considering GCS score for EI had the potential of affecting prognosis in subgroups of patients such as those with trauma surgeries or other surgical categories.
KEY MESSAGES
▪ Patients undergoing endotracheal intubation (EI) had a lower mortality risk compared with similar patients.
▪ Increasing age, systolic blood hypertension, respiratory problems, nosocomial infection, diabetes, history of myocardial infarction, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, immunosuppression, and the use of anesthetics/sedatives/hypnotics during intensive care unit stay are directly associated with mortality.
▪ Considering Glasgow coma scale (GCS) score for EI had the potential of changing prognosis in subgroups of patients.
▪ To decrease the risk of mortality, GCS score should be used for decision making on EI, at least in patients undergoing trauma surgery or other surgical categories.
NOTES
-
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
-
FUNDING
None.
-
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conceptualization: NMM, MF, MD. Data curation: MD, MM. Formal analysis: NMM, SZBJ. Methodology: NMM, SZBJ. Project administration: MF. Writing–original draft: all authors. Writing–review & editing: all authors.
Acknowledgments
None.
Figure 1.Bar chart of Glasgow coma scale (GCS) categories in patients with or without undergoing endotracheal intubation. Intubated patients had a GCS of 10 or less.
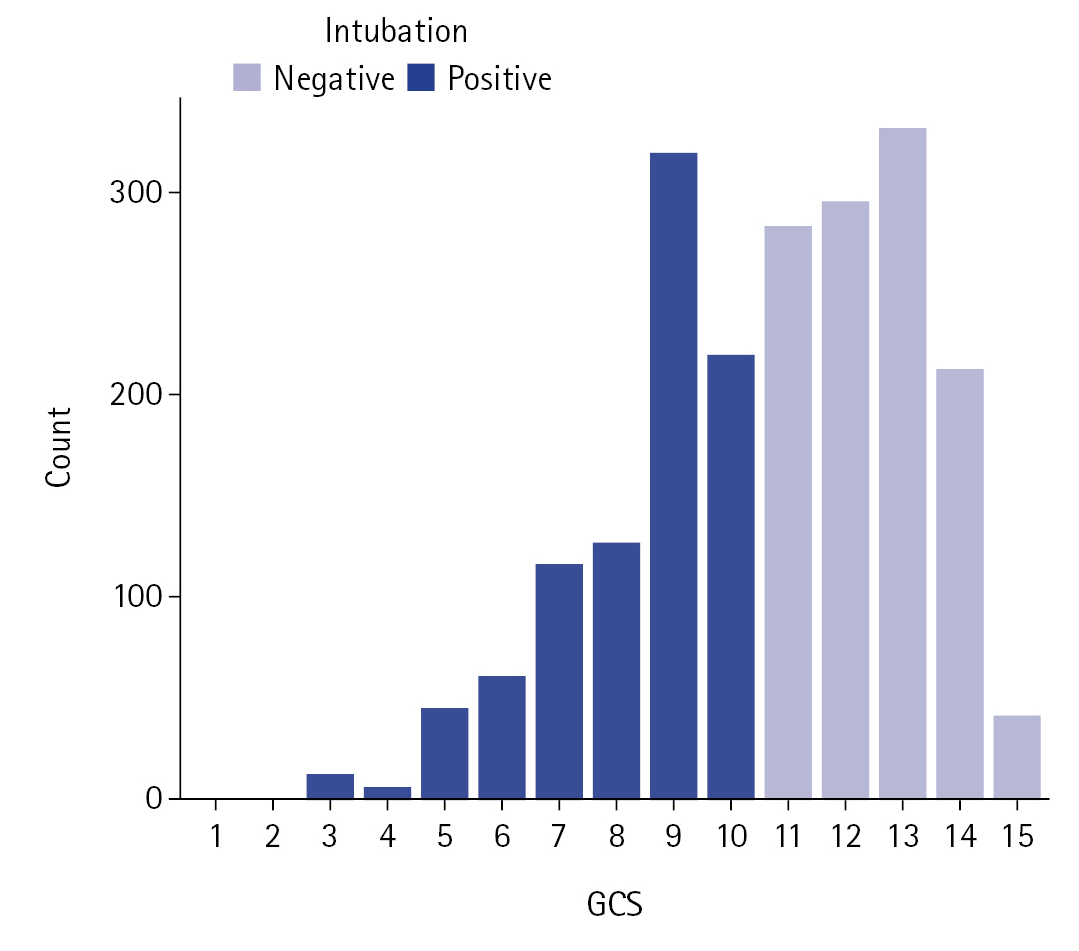
Figure 2.Variable importance for predicting mortality rate. The white boxplots illustrate the confirmed selected features. PaO2: partial pressure of oxygen; PaCO2: partial pressure of carbon dioxide; EI: endotracheal intubation; FiO2: fraction of inspired oxygen; SBP: systolic blood pressure; GCS: Glasgow coma scale; COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; MI: myocardial infarction.
Figure 3.The area under the receiver operator characteristic (ROC) curve (0.81). The black line represents the model prediction and the diagonal gray line denotes the ROC curve of a random classifier.
Table 1.Patients’ characteristics
|
Feature |
Dead group (n=865) |
Discharged group (n=1,190) |
P-value |
|
EI |
355 (41.0) |
538 (45.2) |
0.066b)
|
|
Female |
416 (48.1) |
567 (47.6) |
0.877b)
|
|
Reason for admission |
|
|
<0.001b)
|
|
Elective brain surgery |
108 (12.5) |
159 (13.4) |
|
|
Trauma surgery |
92 (10.6) |
337 (28.3) |
|
Other surgeriesa)
|
140 (16.2) |
296 (24.9) |
|
Respiratory problems |
287 (33.2) |
99 (8.3) |
|
Others |
238 (27.5) |
299 (25.1) |
|
Nosocomial Infection |
201 (23.2) |
106 (8.9) |
<0.001b)
|
|
Surgical patient |
340 (39.3) |
794 (66.7) |
<0.001b)
|
|
Emergency surgery |
191 (22.1) |
432 (36.3) |
<0.001b)
|
|
Diabetes |
446 (51.6) |
185 (15.5) |
<0.001b)
|
|
Myocardial infarction |
292 (33.8) |
99 (8.3) |
<0.001b)
|
|
COPD |
221 (25.5) |
61 (5.1) |
<0.001b)
|
|
Immunosuppression |
175 (20.2) |
120 (10.1) |
<0.001b)
|
|
Anesthetics/sedatives/hypnotics for reasons other than EI |
754 (87.2) |
872 (73.3) |
<0.001b)
|
|
Age (yr) |
61.6±14.3 |
50.2±14.7 |
<0.001c)
|
|
GCS |
10.7±2.5 |
10.7±2.4 |
0.965c)
|
|
SBP (mm Hg) |
113.0±19.4 |
105.5±19.9 |
<0.001c)
|
|
Blood pH |
7.4±0.1 |
7.4±0.1 |
0.071c)
|
|
PaO2
|
69.2±22.7 |
69.2±22.9 |
0.939c)
|
|
PaCO2
|
39.8±11.3 |
39.9±11.4 |
0.935c)
|
|
FiO2
|
45.6±19.6 |
47.8±20.6 |
0.017c)
|
Table 2.The odds ratio for predictors of mortality
|
Predictor |
Adjusted OR |
95% CI |
P-value |
|
EI |
0.32 |
0.11–0.89 |
0.030 |
|
Male |
1.12 |
0.86–1.47 |
0.384 |
|
Elective brain surgery |
1.27 |
0.83–1.95 |
0.266 |
|
Trauma surgery |
1.06 |
0.68–1.63 |
0.808 |
|
Other surgeries |
1.17 |
0.79–1.74 |
0.403 |
|
Respiratory problems |
3.24 |
2.15–4.90 |
<0.001 |
|
Nosocomial infection |
1.64 |
1.11–2.43 |
0.014 |
|
Diabetes |
5.69 |
4.25–7.67 |
<0.001 |
|
History of myocardial infarction |
2.52 |
1.78–3.58 |
<0.001 |
|
COPD |
3.93 |
2.60–6.03 |
<0.001 |
|
Immunosuppression |
3.15 |
2.10–4.76 |
<0.001 |
|
Anesthetics/sedatives/hypnotics for reasons other than EI |
4.60 |
3.18–6.73 |
<0.001 |
|
Age |
1.04 |
1.03–1.06 |
<0.001 |
|
Systolic blood pressure |
1.01 |
1.01–1.02 |
<0.001 |
|
Respiratory rate |
1.01 |
0.93–1.08 |
0.881 |
|
FiO2
|
0.99 |
0.98–1.01 |
0.392 |
|
GCS |
0.84 |
0.76–0.92 |
<0.001 |
|
Intubation×GCS |
1.16 |
0.95–1.42 |
0.144 |
|
Intubation×GCS×elective brain surgery |
1.10 |
0.78–1.54 |
0.573 |
|
Intubation×GCS×trauma surgery |
0.62 |
0.42–0.90 |
0.014 |
|
Intubation×GCS×other surgeries |
0.61 |
0.40–0.93 |
0.024 |
|
Intubation×GCS×respiratory |
0.90 |
0.61–1.34 |
0.624 |
References
- 1. Hatchimonji JS, Dumas RP, Kaufman EJ, Scantling D, Stoecker JB, Holena DN. Questioning dogma: does a GCS of 8 require intubation? Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 2021;47:2073-9.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 2. Nakagawa K, Sagisaka R, Tanaka S, Takyu H, Tanaka H. Early endotracheal intubation improves neurological outcome following witnessed out-of-hospital cardiac arrest in Japan: a population-based observational study. Acute Med Surg 2021;8:e650.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 3. Granfeldt A, Avis SR, Nicholson TC, Holmberg MJ, Moskowitz A, Coker A, et al. Advanced airway management during adult cardiac arrest: a systematic review. Resuscitation 2019;139:133-43.ArticlePubMed
- 4. Jeong S, Ahn KO, Shin SD. The role of prehospital advanced airway management on outcomes for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest patients: a meta-analysis. Am J Emerg Med 2016;34:2101-6.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Dunham CM, Barraco RD, Clark DE, Daley BJ, Davis FE 3rd, Gibbs MA, et al. Guidelines for emergency tracheal intubation immediately after traumatic injury. J Trauma 2003;55:162-79.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Mayglothling J, Duane TM, Gibbs M, McCunn M, Legome E, Eastman AL, et al. Emergency tracheal intubation immediately following traumatic injury: an Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma practice management guideline. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 2012;73(5 Suppl 4):S333-40.PubMed
- 7. Sise MJ, Shackford SR, Sise CB, Sack DI, Paci GM, Yale RS, et al. Early intubation in the management of trauma patients: indications and outcomes in 1,000 consecutive patients. J Trauma 2009;66:32-40.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Duncan R, Thakore S. Decreased Glasgow Coma Scale score does not mandate endotracheal intubation in the emergency department. J Emerg Med 2009;37:451-5.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Jakob DA, Lewis M, Benjamin ER, Demetriades D. Isolated traumatic brain injury: routine intubation for Glasgow Coma Scale 7 or 8 may be harmful! J Trauma Acute Care Surg 2021;90:874-9.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Ribeiro SC. Decreased Glasgow Coma Scale score in medical patients as an indicator for intubation in the Emergency Department: why are we doing it? Clinics (Sao Paulo) 2021;76:e2282.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 11. Fallenius M, Skrifvars MB, Reinikainen M, Bendel S, Raj R. Common intensive care scoring systems do not outperform age and Glasgow Coma Scale score in predicting mid-term mortality in patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage treated in the intensive care unit. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med 2017;25:102. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 12. Knox DB, Lanspa MJ, Pratt CM, Kuttler KG, Jones JP, Brown SM. Glasgow Coma Scale score dominates the association between admission Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score and 30-day mortality in a mixed intensive care unit population. J Crit Care 2014;29:780-5.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 13. McNett M. A review of the predictive ability of Glasgow Coma Scale scores in head-injured patients. J Neurosci Nurs 2007;39:68-75.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Oh TK, Song IA, Jeon YT. Impact of Glasgow Coma Scale scores on unplanned intensive care unit readmissions among surgical patients. Ann Transl Med 2019;7:520. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 15. Markazi-Moghaddam N, Fathi M, Ramezankhani A. Risk prediction models for intensive care unit readmission: a systematic review of methodology and applicability. Aust Crit Care 2020;33:367-74.ArticlePubMed
- 16. Homauni A, Zargar Balaye Jame S, Hazrati E, Markazi-Moghaddam N. Intensive care unit risk assessment: a systematic review. Iran J Public Health 2020;49:1422-31.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 17. Sandri M, Zuccolotto P. Variable selection using random forests. In: Zani S, Cerioli A, Riani M, Vichi M, editors. Data analysis, classification and the forward search. Springer; 2006. p. 263-70.
- 18. Jentzer JC, Murphree DH, Wiley B, Bennett C, Goldfarb M, Keegan MT, et al. Comparison of mortality risk prediction among patients ≥70 versus <70 years of age in a cardiac intensive care unit. Am J Cardiol 2018;122:1773-8.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Wang FD, Chen YY, Chen TL, Lin YT, Fung CP. Risk factors and mortality of nosocomial infections of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in an intensive care unit. J Crit Care 2011;26:82-8.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Adigüzel N, Karakurt Z, Güngör G, Yazicioğlu Moçin O, Acartürk E, Soğukpinar O, et al. Mortality rates and risk factors associated with nosocomial Candida infection in a respiratory intensive care unit. Tuberk Toraks 2010;58:35-43.PubMed
- 21. Skriver MV, Borch-Johnsen K, Lauritzen T, Sandbaek A. HbA1c as predictor of all-cause mortality in individuals at high risk of diabetes with normal glucose tolerance, identified by screening: a follow-up study of the Anglo-Danish-Dutch Study of Intensive Treatment in People with Screen-Detected Diabetes in Primary Care (ADDITION), Denmark. Diabetologia 2010;53:2328-33.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 22. Saydain G, Awan A, Manickam P, Kleinow P, Badr S. Pulmonary hypertension an independent risk factor for death in intensive care unit: correlation of hemodynamic factors with mortality. Clin Med Insights Circ Respir Pulm Med 2015;9:27-33.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 23. Cilli A, Erdem H, Karakurt Z, Turkan H, Yazicioglu-Mocin O, Adiguzel N, et al. Community-acquired pneumonia in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease requiring admission to the intensive care unit: risk factors for mortality. J Crit Care 2013;28:975-9.ArticlePubMed
- 24. Chico-Fernández M, Abelardo Barea-Mendoza J, Servià-Goixart L, Ormazabal-Zabala T, Quintana-Díaz M, González-Robledo J, et al. Factors associated with death due to trauma in patients with a Glasgow Coma Scale score of 3 and bilateral fixed dilated pupils. Emergencias 2021;33:121-7.PubMed
- 25. Bendinelli C, Ku D, King KL, Nebauer S, Balogh ZJ. Trauma patients with prehospital Glasgow Coma Scale less than nine: not a homogenous group. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 2020;46:873-8.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 26. Sepahvand E, Jalali R, Mirzaei M, Ebrahimzadeh F, Ahmadi M, Amraii E. Glasgow Coma Scale versus Full Outline of UnResponsiveness Scale for prediction of outcomes in patients with traumatic brain injury in the intensive care unit. Turk Neurosurg 2016;26:720-4.PubMed
- 27. Leitgeb J, Mauritz W, Brazinova A, Majdan M, Janciak I, Wilbacher I, et al. Glasgow Coma Scale score at intensive care unit discharge predicts the 1-year outcome of patients with severe traumatic brain injury. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg 2013;39:285-92.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 28. Mohammadi T, Mohammadi B. Drawing clinical pictures of heart failure with high mortality risk. Inform Med Unlocked 2021;26:100752. Article
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by

 , Mohammad Fathi2,3
, Mohammad Fathi2,3 , Sanaz Zargar Balaye Jame1
, Sanaz Zargar Balaye Jame1 , Mohammad Darvishi4
, Mohammad Darvishi4 , Morteza Mortazavi1
, Morteza Mortazavi1









 KSCCM
KSCCM
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite




